ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﻜﻪ ﻫﺎي اﺟﺘﻤﺎﻋﻲ ﻣﺠﺎزي
و ﻛﺎرﺑﺮد آن در ﻋﻠﻢ ﺳﻨﺠﻲ
ﺳﻌﻴﺪ اﺳﺪي
ﺳﺮﭘﺮﺳﺖ ﮔﮔﺮوه اﻃﻼ اﻃﻼع ﺳﻨﺠﻲ ﭘﮋوﻫﺸﮕﺎ ﺸﮕﺎه
و ﻋﻀﻮ ﻫﻴﺎت ﻋﻠﻤﻲ داﻧﺸﮕﺎه ﺷﺎﻫﺪ
s.asadi@i di@i d i randoc.ac.irﺷﺒﻜﻪ، ﺷﺒﻜﻪ، ﺑﺤﺚ ﺑﺤﺚ داغ داغ روز
ﺷﺒﮑﻪ ﺳﺎزﯼ
اﻗﺘﺼﺎد ﺷﺒﮑﻪ اﯼ
Networked
Economy
ﮐﺎﻣﭙﻴﻮﺗﺮﯼ
Computer
Networking
ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻗﺎﭼﺎق
Trafficking
Networks
ﺷﺒﮑﻪ ﻣﺒﺎدﻻت ﺑﺎﻧﮑﯽ و
ﻣﺎﻟﯽ
Transaction
N t k
ﺷﺒﮑﻪ ﻧﺨﺒﮕﺎن و
Networks
ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ اﺟﺘﻤﺎﻋﯽ
Social Networks
ﺑﺎزارﻳﺎﺑﯽ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ اﯼ
Network
ﺷﺒﮑﻪ ﻧﺨﺒﮕﺎن و
ﻧﻮﺁورﯼ
Innovation
Networks
ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﮐﺎرﺁﻓﺮﻳﻨﯽ
Entrepreneurial
Networks
Network
Marketing
ﺷﺒﮑﻪ زﻳﺮﺳﺎﺧﺖ هﺎ
Infrastructure
Networks
Network Analysis is the keyword
For the 21
st
Century
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
22ﭘﺮﺳﺶ ﭘﺮﺳﺶﻫﺎي اﺳﺎﺳﻲ
z ﺷﺒﻜﻪ ﻫﺎي اﺟﺘﻤﺎﻋﻲ ﭼﻪ ﻣﻔﻬﻮم، ﺳﺎﺧﺘﺎر و ﻛﺎرﺑﺮدﻫﺎﻳﻲ دارﻧﺪ؟
z ﺷﺒﻜﻪ ﻫﺎي اﺟﺘﻤﺎﻋﻲ در ﻣﺤﻴﻂ اﻳﻨﺘﺮﻧﺖ و وب ﭼﮕﻮﻧﻪ اﻳﺠﺎد و ﺗﻮﺳﻌﻪ ﻣﻲ
ﻳﺎﺑﻨﺪ.
z آﻳﺎ ﻣﻲ ﺗﻮان رﺷﺪ و ﺗﺤﻮﻻت ﺷﺒﻜﻪ ﻫﺎي اﺟﺘﻤﺎﻋﻲ ﻣﺠﺎزي را رﺻﺪ ﻛﺮد و
ﻣﺴﻴﺮﻫﺎ ﻴﺮ يي اﺻﻠﻲ آن را دﻳ ﻲ ن ر ﻳﺪ؟
z آﻳﺎ ﻣﻲ ﺗﻮان ﻗﻮاﻧﻴﻦ ﺣﺎﻛﻢ ﺑﺮ ﻫﻤﻜﺎري در ﻣﺤﻴﻂ ﻫﺎي ﻣﺠﺎزي را اﺳﺘﺨﺮاج
وو اﻧﺪازه اﻧﺪازه ﮔﻴﺮ ﮔ يي ﻛﺮﻛ د؟د؟
z ﻓﻨﻮن ﻛﺘﺎﺑﺴﻨﺠﻲ و ﻋﻠﻢ ﺳﻨﺠﻲ را ﭼﮕﻮﻧﻪ ﻣﻲ ﺗﻮان ﺑﺮاي ﻣﺤﻴﻂ ﻫﺎي
ﻣﺠﺎﺎزي ﻛﺎﻟﻛﺎﻟﻴﺒﺮه ﻛﺮد ﻛ ؟؟
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
33ﺷﺒﻜﻪ ﺷﺒﻜﻪ وب وب ﺟﻬﺎﻧﻲ WWW WWW
وب ﺟﻬﺎﻧﻲ، ﺷﺒﻜﻪ اي ﺑﺴﻴﺎر ﭘﻴﭽﻴﺪه و ﻏﻨﻲ از ﻣﻨﺎﺑﻊ ﻏﻴﺮ ﻫﻤﺴﺎن اﺳﺖ ﻛﻪ ﺑﺎ
ﺑﻬﺮه ﮔﻴﺮي از ﻓﻨﺎوري ﻫﺎ و ﭘﺮوﺗﻜﻞ ﻫﺎي ارﺗﺒﺎﻃﻲ وﻳﮋه، از ﻃﺮﻳﻖ اﻳﻨﺘﺮﻧﺖ ﻗﺎﺑﻞ
دﺳﺘﻴﺎﺑﻲ ﻫﺴﺘﻨﺪ.
وﻳﮋﮔﻲ ﻫﺎي وب:
| ﻣﺤﺘﻮاي ﻮ ي ﭼﻨﺪر ﭼ رﺳﺎﻧﻪ اي وي و ﺗﺮﻛﻴﺒﻲ ﺮ ﻲ
| دﺳﺘﺮﺳﻲ ﺳﺮﻳﻊ و ﺟﻬﺎﻧﻲ
| ﻛﺎرﺑﺮدﻫﺎي رﺑﺮ ي ﺑﺴﻴﺎ ﺑ ﻴ رر درر ﺗﺠﺎﺠ ررت، آﻣﻮزش ﻮزش، ﺳﺮﮔﺮﻣﻲ ﺮ ﺮ ﻲ...
| ﺳﺎﺧﺘﺎر ﭘﻴﻮﻧﺪي ﻓﺮاﻣﺘﻨﻲ
| اﺑﺰار ﺑﺰ ر ﻣﺮﺟﻊ ﺮﺟﻊ و اﻃﻼع و ع رﺳﺎﻧﻲ ر ﻲ
| ارﺗﺒﺎﻃﺎت ﻋﻠﻤﻲ
| دﻧﻴﺎﻫﺎي ﻣﺠﺎزي
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
44وب وب ﺑﻪ ﺑﻪ ﻋﻨﻮان ﻋﻨﻮان ﻳﻚ ﻳﻚ ﺣﻮزه ﺣﻮزه ﻣﻄﺎﻟﻌﺎﺗﻲ ﻣﻄﺎﻟﻌﺎﺗﻲ
z ﻣﻄﺎﻟﻌﺎت اوﻟﻴﻪ ﺑﺮ ﺳﺎﺧﺘﺎر ﭘﻴﻮﻧﺪﻫﺎي ﻓﺮاﻣﺘﻨﻲ اﺳﺘﻮار ﺑﻮد.
| ﺑﺮآﻳﻨﺪ ﻣﻄﺎﻟﻌﺎت دوره اول اﻳﺠﺎد ﻣﻮﺗﻮرﻫﺎي ﺟﺴﺘﺠﻮي ﻓﺮاﭘﻴﻮﻧﺪي ﺑﻪ وﻳﮋه ﮔﻮﮔﻞ
ﺑﻮد.
z ﻣﻄﺎﻟﻌﺎت ﻓﺎز دوم ﺑﺮ وب ﻋﻤﻴﻖ، دﺳﺘﺮس ﭘﺬﻳﺮﺳﺎزي ﺑﺮﻧﺎﻣﻪ ﻫﺎي ﻛﺎرﺑﺮدي
از ﻃﺮﻳﻖ ﺷﺒﻜﻪ وب و ﺑﻪ ﻛﺎرﮔﻴﺮي وب ﺑﺮاي ارﺗﺒﺎﻃﺎت، ﺗﺒﻠﻴﻐﺎت و ﺑﺎزارﻳﺎﺑﻲ
اﺳﺘﻮار ﺑﻮد.
| ﺑﺮآﻳﻨﺪ اﻳﻦ ﻣﻄﺎﻟﻌﺎت ﮔﺴﺘﺮش وﺑﺴﺎﻳﺖ ﻫﺎ، اﻳﺠﺎد ﺧﺪﻣﺎت ﻣﺘﻌﺪد ﺑﺎﻧﻜﻲ، آﻣﻮزش
ﻫﺎي ﻣﺠﺎزي و ﻣﻮﺗﻮرﻫﺎي ﺟﺴﺘﺠﻮي ﻣﻌﻨﺎﻳﻲ ﺑﻮد.
z ﺳﻮﻣﻴﻦ ﻓﺎز از ﻣﻄﺎﻟﻌﻪ ﺑﺮ روي ﻣﺤﻴﻂ وب ﻣﺮﺑﻮط ﺑﻪ ﮔﺴﺘﺮش ﻣﺸﺎرﻛﺖ
ﻛﺎرﺑﺮان در ﺗﻮﻟﻴﺪ و ﺳﺎﻣﺎﻧﺪﻫﻲ ﻣﺤﺘﻮاي وب ﺑﻮده اﺳﺖ.
| ﺑﺮآﻳﻨﺪ آن اﻳﺠﺎد اﻣﻜﺎﻧﺎت وب 2 و ﻣﺤﺘﻮاي ﻛﺎرﺑﺮ ﻣﺪار ﺑﻮده اﺳﺖ.
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
55ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
66
Î Web 2.0ﺣﻮزه ﺣﻮزه ﻫﺎي ﻫﺎي ﻛﻼن ﻛﻼن دردر ﻣﻄﺎﻟﻌﻪ ﻣﻄﺎﻟﻌﻪ وب وب
z ﻣﻄﺎﻟﻌﺎت ﻓﻨﻲﻲ وو زﻳﺮﺳﺎﺧﺘﻲ زﻳﺮ ﻲ
z ﻣﻮﺗﻮرﻫﺎي ﺟﺴﺘﺠﻮ و ﺑﺎزﻳﺎﺑﻲ اﻃﻼﻋﺎت
zz ﺧﺪﻣ ﺧﺪ ﺎت ﺎت ﻛﺘﺎﺑ ﻛﺘﺎ ﺨﺎﻧﻪ ﺨﺎﻧﻪ ااي و اﻃﻼع اﻃﻼع رﺳﺎﻧﺎﻧﻲ
z ﻛﺎرﺑﺮدﻫﺎي وب در ﺗﺠﺎرت، ﺑﺎزارﻳﺎﺑﻲ، ﺧﺪﻣﺎت...
z ﺷﺎﺧﺺﻫﺎي اﻧﺪازهﮔﻴﺮي وب
z ﺛﺒﺎت،اﻋﺘﺒﺎر، رواﻳﻲﻲ ﻣﺤﺘﻮاﻳﻲ ﻮ ﻲ وب
z ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﭘﻴﻮﻧﺪﻫﺎي وب
z ارﺗﺒ ا ﺗ ﺎﻃﺎت ﺎﻃﺎت ﻋﻠﻋﻠﻤﻲ
z ﺷﺒﻜﻪ ﻫﺎي اﺟﺘﻤﺎﻋﻲ ﻣﺠﺎزي
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
77وب وب ﺳﻨﺠﻲ Webometrics Webometrics
«وبﺳﻨﺠﻲ ﻋﺒﺎرت اﺳﺖ از ﻣﻄﺎﻟﻌﻪ ﺟﻨﺒﻪﻫﺎي ﻛﻤﻲ ﺳﺎﺧﺘﺎر و اﺳﺘﻔﺎده از
ﻣﻨﺎﺑﻊ اﻃﻼﻋﺎﺗﻲ، ﺗﺮﻛﻴﺐ و ﻓﻨﺎوريﻫﺎي ﺑﻪ ﻛﺎر رﻓﺘﻪ در وب، ﻛﻪ ﺑﺎ اﻟﮕﻮﮔﻴﺮي
از ﺷﻴﻮهﻫﺎي ﻛﺘﺎبﺳﻨﺠﻲ و اﻃﻼع ﺳﻨﺠﻲ ﺻﻮرت ﻣﻲﮔﻴﺮد»
4 ﺣﻮزﻮزه ﻣﻄﺎﻟﻌﺎﺗﻲﻲ اﺻﻠﻲﻲ درر ﻣﻄﺎﻟﻌﺎت ووب ﺳﻨﺠﻲﻲ:
|ﺗﺠﺰﻳﻪ و ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﻛﻤﻲ و ﻛﻴﻔﻲ ﻣﺤﺘﻮاي ﺻﻔﺤﺎت وب
||ﺗﺠﺰﻳﻪ ﺗﺠﺰﻳﻪ وو ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﻛﻤﻛﻤﻲ وو ﻛﻴﻔ ﻛﻴﻔﻲ ﺳﺎﺧﺘﺎر ﺳﺎﺧﺘﺎر ﭘﻴﻮﻧﺪﻫﺎي ﭘﻴﻮﻧﺪﻫﺎي وﺑوﺑﻲ
|ﺗﺠﺰﻳﻪ و ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﻣﻴﺰان اﺳﺘﻔﺎده از وب ( از ﻃﺮﻳﻖ ﻓﺎﻳﻞ ﮔﺰارش وب)
||ﺗﺠﺰﻳﻪ و ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻠ ﻞﻞ ﻓﻨﺎورﻳﻬ ﻓ ﺎ ﺎﺎي وب ((ﺷﺎﻣﺎ ﻞﻞ ارزﻳ ا ﺎﺎﺑﻲ ﻋﻤﻠﻜ ﻠﻜﺮد ﻣﻮﺗﻮرﻫﺎﺎ))
ﺑﻴﻮرنﺑﺮن و اﻳﻨﮕﻮرﺳﻦ (2004 )
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
88ﻣﻄﺎﻟﻌﺎت ﻣﻄﺎﻟﻌﺎت ﺟﻐﺮاﻓﻴﺎﻳﻲ ﺟﻐﺮاﻓﻴﺎﻳﻲ
z در ﺣﺎل ﺣﺎﺿﺮ ﻣﻴﺰان اﺳﺘﻔﺎده و ﺿﺮﻳﺐ ﻧﻔﻮذ اﻳﻨﺘﺮﻧﺖ، ﻳﻜﻲ از ﺳﻨﺠﻪﻫﺎﻳﻲ اﺳﺖ ﻛﻪ از
ﻃﺮﻳﻃ ﻖﻖ آن آن وﺿﻌﻴﺿ ﺖﺖ ﻓﺮﻓ ﻫﻨﮕ ﻫﻨﮕﻲ، ﻋﻠﻋﻠﻤﻲ، اﺟﺘﻤ ا ﺘ ﺎﻋﺎﻋﻲ ﻲو رﻓﺎﻫ ﻓﺎﻫ ﻛﺸﻮر ﻛﺸ ﻫﺎﻫﺎ راا ﻣﻲﺳﻨﺠ ﻨ ﻨﺪ ﻨﺪ.
zz ﺑﻨﺎﺑﺮاﻳﻦ، ﺑﻨﺎﺑﺮاﻳﻦ، ﻛﺸﻮري ﻛﺸﻮري ﻛﻪﻛﻪ ﻣﻴﺰان ﻣﻴﺰان ﺣﻀﻮر ﺣﻀﻮر ﺑﻴﺸﺘﺮي ﺑﻴﺸﺘﺮي دردر اﻳﻦ اﻳﻦ ﻣﺤﻴﻂ ﻣﺤﻴﻂ داﺷﺘﻪ داﺷﺘﻪ ﺑﺎﺷﺪ، ﺑﺎﺷﺪ، ﻧﺸﺎﻧﮕﺮ ﻧﺸﺎﻧﮕﺮ ﺗﻮﺳﻌﻪ ﺗﻮﺳﻌﻪ
و ﺷﻜﻮﻓﺎﻳﻲ ﻋﻠﻢ و ﻓﻨﺎوري در آن ﻛﺸﻮر اﺳﺖ
.
z از ﺳﻮي دﻳﮕﺮ، ﻫﺮ ﭼﻪ ﻣﻴﺰان ﺣﻀﻮر ﻛﺸﻮري در ﻣﺤﻴﻂ وب ﺑﻴﺸﺘﺮ ﺑﺎﺷﺪ، ﻳﻌﻨﻲ
ﺳﺎﻳﺖﻫﺎي ﻋﻠﻤﻲ، ﺗﺠﺎري و ارﺗﺒﺎﻃﻲ ﻓﻌﺎل و ﮔﺴﺘﺮدهاي داﺷﺘﻪ ﺑﺎﺷﺪ، اﻳﻦ ﻛﺸﻮر
اﻣ ا ﻜﺎﻧﺎت ﻜﺎﻧﺎت ارﺗﺒ ا ﺗ ﺎﻃ ﺎﻃﻲ ﺑﻬﺘﺘﺮي ﺑﺎﺎ ﺳﺎﺎﻳﺮ ﻛﺸﻮرﻫ ﻛﺸ ﺎﺎ يوداﺷﺘ اﺷﺘﻪ ﻛﺸﻮرﻫ ﻛﺸ ﺎﺎ دﻳﮕﮕﺮ ﻣﻲﺗﻮﺗ اﻧاﻧﻨﺪ ﺑﻪ ﺗﺒﺎد ﺗ ﺎ ﻻت ﻻت
ﮔﻮﻧﺎﮔﻮﻧﻲ ﺑﺎ اﻳﻦ ﻛﺸﻮر ﺑﭙﺮدازﻧﺪ ﻛﻪ ﻫﻤﻪ ﺑﻪ رﺷﺪ ﺑﻴﺸﺘﺮ آن ﻛﺸﻮر ﻛﻤﻚ ﻣﻲﻛﻨﻨﺪ.
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
99اﻧﮕﻴﺰه اﻧﮕﻴﺰه ﻫﺎي ﻫﺎي ﭘﻴﻮﻧﺪ ﭘﻴﻮﻧﺪ دادن
z ﭘﻴﻮﻧﺪﻫﺎ را ﻣﻬﻤﺘﺮﻳﻦ ﻋﺎﻣﻞ ارﺗﺒﺎﻃﻲ ﺑﻴﻦ ﻣﻨﺎﺑﻊ ﻣﺤﻴﻂ وب ﻣﻲداﻧﻨﺪ .
z ﭘﻴﻮﻧﺪﻫﺎﺎ، ﻲﻳﻚﻚ وﻳﮋﮔﮔ ﺑﺴﻴﺎﺎر ﻣﻬﻢ ﺑﻪ ﻣﻨﺎﺎﺑﻊ وب اﻓاﻓﺰودﻧﺪ ﻛﻛﻪ در ﻫﻴﭻ زﻳﻚﻚ اا ﻣﻨﺎﺎﺑﻊ
اﻃﻼﻋﺎﺗﻲ ﻗﺒﻞ از آنﻫﺎ ﻳﺎﻓﺖ ﻧﻤﻲﺷﻮد و آن ﻋﻤﻖ دادن ﺑﻪ ﻣﻨﺎﺑﻊ اﺳﺖ
zz ﻫﻫﺮ ﭘﻴﭘ ﻮﻧﺪي ﻮﻧﺪي ﻛﻪﻛﻪ ددر ﻣﺤﻴ ﻣﺤ ﻂﻂ وب وب اﻳﺠﺎد اﻳﺠﺎد ﻣﻣﻲﺷﻮد، ﺷﻮد، ﻣﺒﻣ ﺘﻨﺘﻨﻲ ﺑﺑﺮ ﻫﺪﻓ ﻫﺪﻓﻲ ﺷﻜﻞ ﺷﻜﻞ ﮔﺮﮔ ﻓﺘﻪ ﻓﺘﻪ اﺳﺖ اﺳﺖ ((link link
(motivations
z ﻛﻪﻫﻤﺎنﮔﻮﻧﻪ از ﻃﺮﻳﻖ اﺳﺘﻨﺎدﻫﺎي ﻣﻨﺎﺑﻊ ﻣﻜﺘﻮب ﻣﻲﺗﻮان ﺳﺎﺧﺘﺎر ﺗﻮﺳﻌﻪ ﻋﻠﻢ ﻳﻚ
ﻣﻮﺿﻮع ﻳﺎ ﻛﺸﻮر و ﻏﻴﺮه را ﺗﺮﺳﻴﻢ ﻧﻤﻮد، از ﻃﺮﻳﻖاﻳﻦ ﻧﻴﺰ ﻣﻲﺗﻮان ارﺗﺒﺎﻃﻲاﻟﮕﻮﻫﺎي و
ﺗﻮﺳﻌﻪ ﻋﻠﻢ در ﻣﺤﻴﻂ وب را ﺷﻨﺎﺳﺎﻳﻲ و ﺗﺮﺳﻴﻢ ﻛﺮد .
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
1010ﺷﺒﻜﻪ ﺷﺒﻜﻪ ﻫﺎي ﻫﺎي اﺟﺘﻤﺎﻋﻲ Social Social Networks Networks
ﺷﺒﻜﻪ ﻫﺎي اﺟﺘﻤﺎﻋﻲ ي ﻲ ﮔﺮوﻫﻲ ﺮو ﻲ از اﻓﺮ ز ﺮاد ﻳﺎ ﺳﺎزﻣﺎن ز ن ﻫﺎيي داراي ر ي ﺳﻠﻴﻘﻪ ﻳﺎ ﻣﻨﺎﻓﻊﻊ
ﻣﺸﺘﺮك ﻫﺴﺘﻨﺪ ﻛﻪ ﺑﺮاي دﺳﺘﻴﺎﺑﻲ ﺑﻪ اﻫﺪاف ﺧﺎﺻﻲ ﮔﺮد ﻣﻲ آﻳﻨﺪ. ﻫﺮ ﻋﻀﻮ را ﻳﻚ
ﺑﺎزﻳﮕﺮ (actor) ﻣﻲ ﮔﻮﻳﻨﺪ. وﻳﮋﮔﻲ ﺷﺒﻜﻪ ﻫﺎي اﺟﺘﻤﺎﻋﻲ وﺟﻮد رواﺑﻂ
((relationship relationship)) و ﺗﻌﺎﻣﺎ ﻼﻼت ((interaction interaction)) ﭘﻴﭽﻴﺪه ﺑﻴﻦ ﺑﺎزﻳﮕﺮا ﺎ ﮕ ان ااﺳﺖ.
دﻻﻳﻞ ﻻ ﻞ ﻋﻤﺪه اﻳﺠﺎ ا ﺎد ﺷﺒﻜﻪ ﻫﺎ ﻜ ﺎي اﺟﺘﻤ ا ﺎﺎﻋﻲ:
z رواﺑﻂ ﻓﺮدي
z رواﺑا ﻂﻂ ﻛﺎري
z رواﺑﻂ ﻋﻠﻤﻲ
z ﺳﻠﻴﻘﻪ ﻫﺎ و ﻋﻼﻳﻖ و ﺗﻔﺮﻳﺤﺎت ﻣﺸﺘﺮ ﻠ ﺎ ﻼ ﺎ كك
z اﻧﮕﻴﺰه ﻫﺎي اﺟﺘﻤﺎﻋﻲ - ﺳﻴﺎﺳﻲ
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
1111ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﻜﻪ ﺷﺒﻜﻪ ﻫﺎي ﻫﺎي اﺟﺘﻤﺎﻋﻲ اﺟﺘﻤﺎﻋﻲ SNA SNA
آﻧﺎﻟﻴﺰ ﻳﺎ ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﻜﻪ ﻫﺎي اﺟﺘﻤﺎﻋﻲ ﺑﻪ ﻣﻌﻨﺎي ﺰ ﻞ ي ﻲ ي ﻣﻄﺎﻟﻌﻪ وﻳﮋﮔ و ﮋ ﻲﻲ ﻫﺎي ﺷﺒﻜﻪ ﻫﺎي ي ي
اﺟﺘﻤﺎﻋﻲ و رواﺑﻂ ﺑﻴﻦ اﻓﺮاد و ﺑﺨﺶ ﻫﺎي ﻳﻚ ﺷﺒﻜﻪ ﺑﺎ روﻳﻜﺮد ﺗﺌﻮري ﺷﺒﻜﻪ اي ﻳﺎ
ﮔﺮاف اﺳﺖ.
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﻜﻪ ﺷﺒﻜﻪ ﻫﺎي اﺟﺘﻤﺎﻋﻲ ﻧﻮﻋﻲ ﻣﻄﺎﻟﻌﻪ ﻣﻴﺎن رﺷﺘﻪ اي در ﺣﻮزه ﻫﺎي
ﻣﺨﺘﻠﻒ اﺳﺖ، از ﺟﻤﻠﻪ:
ﺟﺎﻣﻌﻪ ﺷﻨﺎﺳﻲ، ﻋﻠﻮم اﻃﻼﻋﺎت، ﻋﻠﻮم ارﺗﺒﺎﻃﺎت، ﻣﺪﻳﺮﻳﺖ و ﺳﺎزﻣﺎن، اﻧﺴﺎن
ﺷﻨﺎﺳﻲ ﺷﻨﺎﺳ ،، ﺟﻐﺮاﻓﻴﺎ، ﺟﻐﺮاﻓﻴﺎ، رواﻧﺸﻨﺎﺳ رواﻧﺸﻨﺎﺳﻲ اﺟﺘﻤﺎﻋﻲ اﺟﺘﻤﺎﻋ ،، زﺑﺎن زﺑﺎن ﺷﻨﺎﺳﻲ، ﺷﻨﺎﺳ ، اﭘﻴﺪﻣﻴﻮﻟﻮژي، اﭘﻴﺪﻣﻴﻮﻟﻮژي، اﻗﺘﺼﺎد اﻗﺘﺼﺎد
و ﺑﺎزرﮔﺎﻧﻲ
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
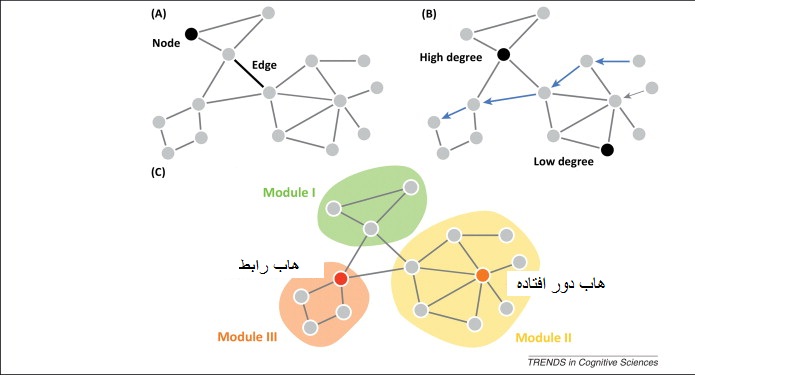
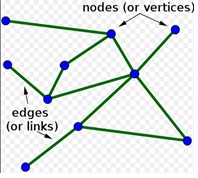
1212Graph Graph Theory Theory ﮔﺮاف ﺗﺌﻮري
ﻣﺠﻤﻮﻋﻪ اي از ﻗﻮاﻋﺪ ﻮ ي ز ﻮ وو دﻳﺪﮔﺎﻫﻬﺎﻬ يي اﺳﺖ ﻛﻪ درر ﻋﻠﻮمﻮم ﻛﺎﻣﭙﻴﻮﺗﺮ ﭙ ﻮ ﺮ و ر و رﻳﺎﺿﻴﺎت
ﻛﺎرﺑﺮدي، در ﻣﻄﺎﻟﻌﻪ ﺗﻤﺎم ﻳﺎ ﺑﺨﺸﻲ از اﻋﻀﺎي ﻳﻚ ﻣﺠﻤﻮﻋﻪ در ﻗﺎﻟﺐ ﮔﺮاف ﻳﺎ
ﻧﻤﻮدارﻫﺎي داراي اﺗﺼﺎل ﻛﺎرﺑﺮد دارﻧﺪ. اﻓﺮاد را در اﻳﻦ دﻳﺪﮔﺎه راس ﻳﺎ ﮔﺮه و رواﺑﻂ
را ﻳﺎل ﻳ ا ﺎل ﺎﺎ ﭘﻴﻮﻧﻧﺪ ﻳﺎ ﻟﺒﻪ ﻣﻲ ﺎ ﻟ ﮔﮔﻮﻳﻨﺪ.
actor actor
relationship
node
edge
node
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
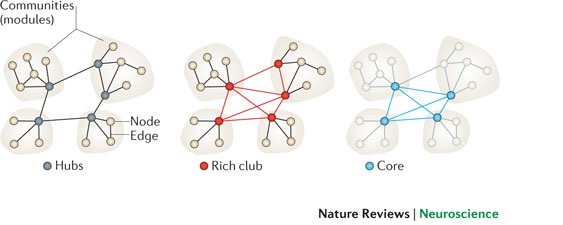
1313ﻓﺮد، ﮔﺮوه و ﺷﺒﻜﻪ
z ﺷ ﻜﻪ (Network) ﻋﻪ ا از اﻓ اد ا ﺖ
ﻓﺮد، ﮔﺮوه و ﺷﺒﻜﻪ
z ﺷﺒﻜﻪ (Network) ﻣﺠﻤﻮﻋﻪ اي از اﻓﺮاد اﺳﺖ.
z ﻓﺮد (Individual) در ﻳﻚ ﺷﺒﻜﻪ اﺟﺘﻤﺎﻋﻲ ﻧﻘﺶ ﺑﺎزﻳﮕﺮ (Player) را دارد.
z اﻓﺮاد ﻳﻚ ﺷﺒﻜﻪ ﻣﻤﻜ ﺮ ﻳ ﺒ ﻦﻦ اﺳﺖ ﮔﺮوﺮوه ﻫﺎ ﻳﺎ اﺟ ﻳ ﺟﺘﻤﺎﻋﺎت ((Communities)) ﻛﻮﭼﻜﺘﺮي ﻮﭼ ﺮي
ﺗﺸﻜﻴﻞ دﻫﻨﺪ.
Role
Position
PP ti restige
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
1414ﺷﺎﺧﺺ ﺷﺎﺧﺺﻫﺎي ﻫﺎي اﺻﻠﻲ اﺻﻠﻲ ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﻜﻪ ﺷﺒﻜﻪ اﺟﺘﻤﺎﻋﻲ اﺟﺘﻤﺎﻋﻲ
1. Degree Degree Centrality: Centrality:
The number of direct connections a node has. What
those connections lead to and how really matters is where
unconnectt ded. thth t th th i ey connect the otherwise
2. Betweenness Centrality:
A node with high betweenness has great influence over what
network indicating important links and flows in the
single point of failure.
3.. Closeness Centrality: Closeness Centrality:
The measure of closeness of a node which are close to
everyone else.
The The pattern of the direct and indirect ties allows the nodes pattern of the direct and indirect ties allows the nodes
the network more quickly than any other node in
all others. anyone else. They have the shortest paths to
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
1515اﺗﺼﺎل Connection
Size z
Number of nodes |
Density z
Number of ties that are present the amount of ties |
that could be present
Out-degree z
Sum Sum of connections from an actor to others of connections from an actor to others |
In-degree z
Sum of connections to an actor |
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
1616ﻓﺎﺻﻠﻪ Distance
Walk z
A sequence of actors and relations that begins and |
ends with actors
GG d i di t eodesic distance z
The number of relations in the shortest possible walk |
from from one actor to another one actor to another
Maximum flow z
The The amount of different actors in the neighborhood of amount of different actors in the neighborhood of |
a source that lead to pathways to a target
Sum of connections to an actor |
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
1717ﻗﺪرت ﻗﺪرت وو ﭘﺮﺳﺘﻴﮋ Power Power & Prestige & Prestige
Walk z
A sequence of actors and relations that begins and |
ends with actors
GG d i di t eodesic distance z
The number of relations in the shortest possible walk |
from from one actor to another one actor to another
Maximum flow z
The The amount of different actors in the neighborhood of amount of different actors in the neighborhood of |
a source that lead to pathways to a target
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
1818ﻗﺪرت ﻗﺪرت وو ﭘﺮﺳﺘﻴﮋ Power Power & Prestige & Prestige
Walk z
A sequence of actors and relations that begins and |
ends with actors
GG d i di t eodesic distance z
The number of relations in the shortest possible walk |
from from one actor to another one actor to another
Maximum flow z
The The amount of different actors in the neighborhood of amount of different actors in the neighborhood of |
a source that lead to pathways to a target
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
1919ﻗﺪرت ﻗﺪرت وو ﭘﺮﺳﺘﻴﮋ Power Power & Prestige & Prestige
Microsoft Bash Asha
Kentaro Ranjeet
Sharad Yale New York City
Ranjeet and I already had a friend in common!
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
2020ﻗﺪرت ﻗﺪرت وو ﭘﺮﺳﺘﻴﮋ Power Power & Prestige & Prestige
p = 0 0 ; k = 0
Erdős and Renyi (1959)
p 0.0 ; k 0
p = 0.09 ; k = 1
p = 0.045 ; k = 0.5
Let’s look at…
p = 1.0 ; k ≈ N
Size of the largest connected cluster
Diameter Diameter (maximum path length between nodes) of the largest cluster (maximum path length between nodes) of the largest cluster
Average path length between nodes (if a path exists)
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
2121ﻗﺪرت ﻗﺪرت وو ﭘﺮﺳﺘﻴﮋ Power Power & Prestige & Prestige
Rao
Kentaro Ranjeet
Bash
Sharad
Anandan Prof. Sastry
Prof. McDermott
Venkie
Prof. Balki
Ravi’s
Father
Prof.
Kannan
Prof. Veni
Karishma
Maithreyi
Pres. Kalam
Ravi
Pawan
Father
Prof. Prahalad
PM Manmohan
Singh
Prof. Jhunjhunwala
Dr. Isher Judge
Ahluwalia
Aishwarya
Amitabh
Soumya
Dr. Montek Singh
Ahluwalia
Ahluwalia
Nandana Bachchan
Sen
Prof. Amartya
Sen
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
2222Random Graphs
N = 12
Random Graphs
Erdős and Renyi (1959)
p = 0 0 ; k = 0
N nodes
p 0.0 ; k 0
A pair of nodes has
probability p of being
connected.
Average degree k ≈ pN
p = 0.09 ; k = 1
Average degree, k ≈ pN
What interesting g g things can
be said for different values
of p or k ?
(that are true as N Æ ∞)
p = 1.0 ; k ≈ N
(that are true as N Æ ∞)
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
2323Random Random Graphs Graphs
Erdős and Renyi (1959)
pp = 00.00 ;; kk = 00
p = 0.09 ; k = 1
p = 0.045 ; k = 0.5
Let’s look at…
p = 1.0 ; k ≈ N
Size of the largest connected cluster
Diameter Diameter (maximum path length between nodes) of the largest cluster (maximum path length between nodes) of the largest cluster
Average path length between nodes (if a path exists)
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
2424Random Random Graphs Graphs
Erdős and Renyi (1959)
p = 0.0 ; k = 0 p = 0.045 ; k = 0.5 p = 0.09 ; k = 1 p = 1.0 ; k ≈ N
Size of larg p gest component
Diameter of largest component
1 5 11 12
0 4 7 1
Average path length between (connected) nodes
0.0 2.0 4.2 1.0
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
2525Semantic social networks
Millions of FOAF profiles
online
http://sioc-project.org/node/158 ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ هﺎﯼ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ
2626Social tagging
SCOT
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
2727SNA on the semantic web
[Paolillo and Wright 2006]
Foaf:knows
Foaf:interest
Rich graph representations reduced to simple
untyped untyped graphs in order to apply SNA graphs in order to apply SNA
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
2828Social Network Analysis?
A science to understand the structure the z
[Wasserman & Faust 1994] [Scott 2000] [Mika 2007]
A science to understand the structure, the
interactions and the strategic positions in social
networks.
SS i ociograms z
[Moreno, 1933]
What for? z
To control information flow |
ToTo improve/stimulate communication improve/stimulate communication |
To improve network resilience |
To trust |
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
2929Centrality: strategic positions
Degree centrality:
[Freeman 1979]
Degree centrality:
Local attention
Closeness centrality:
Capacity Capacity toto
communicate
beetweenness centrality:
reveal broker
"AA place for good ideas place for good ideas"
[Burt 1992] [Burt 2004]
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
3030BB l Th alance Theory
[Heider 1958]
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
3131ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﻜﻪ ﺷﺒﻜﻪ ﻫﺎي ﻫﺎي اﺟﺘﻤﺎﻋﻲ اﺟﺘﻤﺎﻋﻲ ... ...
•Networks are structurally cohesive if they remain connected even when nodes are
removed
0 1 2 3
Node Connectivity
0 1 2 3
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
3232ﺷﺎﺧﺺ ﺷﺎﺧﺺﭼﺴﺒﻨﺪﮔﻲ ﺳﺎﺧﺘﺎر
Fo a de t o o St uctu a Co es o ormal definition of Structural Cohesion: z
A group’s structural cohesion is equal to the minimum (a)
number of actors who, if removed from the g p group, would
disconnect the group.
Equivalently (by Menger’s Theorem): z
A group’s structural cohesion is equal to the minimum (b)
number of independent paths linking each pair of actors
in the group.
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
3333ﺷﺎﺧﺺ ﺷﺎﺧﺺﭼﺴﺒﻨﺪﮔﻲ ﭼﺴﺒﻨﺪﮔﻲ ﺳﺎﺧﺘﺎر ... ...
Structural cohesion gives rise automatically to a clear notion of
embeddedness, since since cohesive sets nest inside of each other cohesive sets nest inside of each other.
2
8 10
9
4
1 3
11
14
12
13
5 7
6
17
18
19
14
15
16
6
20
2
22
23
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
3434ﺳﺎﺧﺘﺎر ﺳﺎﺧﺘﺎر ﻣﻮﺿﻮﻋﻲ ﻣﻮﺿﻮﻋﻲ ﻣﻘﺎﻻت ﻣﻘﺎﻻت ﻣﺠﻼت ﻣﺠﻼت ﻋﻠﻤﻲ ﻋﻠﻤﻲ ﭘﮋوﻫﺸﻲ ﭘﮋوﻫﺸﻲ
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
3535ﻣﺼﻮرﺳﺎزي ﺷﺒﻜﻪ اﺟﺘﻤﺎﻋﻲ
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
3636ﭼﺎﻟﺶ ﭼﺎﻟﺶﻫﺎي ﻫﺎي ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﻜﻪ ﺷﺒﻜﻪ اﺟﺘﻤﺎﻋﻲ اﺟﺘﻤﺎﻋﻲ
If the citation networks capture the structure of organized disciplines, how do we z
capture thh i l i i f di i li d h bl ? e internal organization of disciplines around research problems?
Could use paper citation networks (see Hargens 2000), but data are difficult & •
expensii t bt i f l ve to obtain for large-scall t k e networks.
Can examine the network of papers formed by the topics they write about. •
Di Di tl t i tifi t t rectly taps scientific content •
Purely endogenous creation of topics that allows new topic areas to emerge •
and old ones to die over time
DD t b t t d f i f ti h ld i ata can be extracted from information held in SS i l i l Ab t t ociological Abstracts •
Multiple levels: •
Coarse grainedÆ Focus solely on keywords •
Fine grained Æ Use all information available (title, abstract, •
keywords)
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
3737ﺷﺒﻜﻪ ﺷﺒﻜﻪ ﻫﺎي ﻫﺎي اﺟﺘﻤﺎﻋﻲ اﺟﺘﻤﺎﻋﻲ وو وب وب
Social Social network analysis is useful for the Web network analysis is useful for the Web z
because the Web is essentially a virtual society, and
thus a virtual social network,
Each page: a social actor and |
each hyperlink: a relationship. |
Many results from social network can be adapted z
and extended for use in the Web context.
We study two types of social network analysis, z
centralityy and p g prestige, which are closely related to
hyperlink analysis and search on the Web.
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
3838ﻣﺮﻛﺰﻳﺖ Centrality
Impo ta t o p o e t acto s portant or prominent actors a e t ose t at a e ed are those that are linked z
or involved with other actors extensively.
A p ( person with extensive contacts (links) or z
communications with many other people in the
organization is considered more important than a person
withith l ti l f t t relatively fewer contacts.
The links can also be called ties. A central actor is one z
involved involved in many ties in many ties.
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
3939درﺟﻪ ﻣﺮﻛﺰﻳﺖ Centrality
z ﭘﻴﻮﻧﺪﻫﺎي ﭘ ﻮ ي ﻳﻚ ﺳﻮﻮﻳﻪ
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
4040ﻧﺰدﻳﻜﻲ Closeness
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
4141ﻣﻴﺎن ﺑﻮدن Middleness
IfIf two non two non-adjacent adjacent actors actors jj and and kk want want toto zz
interact and actor i is on the path between j and
k, then then ii may may have some control over the have some control over the
interactions between j and k.
Betweenness Betweenness measures measures this control of this control of ii over over zz
other pairs of actors. Thus,
ifif ii isis on the paths of many such interactions then on the paths of many such interactions, then ii isis ||
an important actor.
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
4242ﭘﺮﺳﺘﻴﮋ Prestige
Prestige Prestige is a more refined measure of prominence of is a more refined measure of prominence of z
an actor than centrality.
Disting ( guish: ties sent (out-links) ( ) and ties received (in-links). |
A prestigious actor is one who is object of extensive z
ties as a recipient.
To compute the prestige: we use only in-links. |
Diffe e ce bet ee ce t a ty a d p est ge erence between centrality and prestige: z
centrality focuses on out-links |
p g prestige focuses on in-links. |
We study three prestige measures. Rank prestige z
forms the basis of most Web p g y page link analysis
algorithms, including PageRank and HITS.
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
4343ﻣﺠﺎورت Proximity
The The degree index of prestige of an actor degree index of prestige of an actor ii only only z
considers the actors that are adjacent to i.
The proximity proximity prestige prestige generalizes generalizes it by considering it by considering z
both the actors directly and indirectly linked to actor
i.
We consider every actor j that can reach i. |
Let I
i
be the set of actors that can reach actor i. z
The proximity is defined as closeness or distance z
of of other actors to other actors to ii..
Let d(j, i) denote the distance from actor j to actor i. z
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
4444رﺗﺒﻪ Rank
InIn the previous two prestige measures, an important the previous two prestige measures, an important z
factor is considered,
the pprominence of individual actors who do the “voting” |
In the real world, a person i chosen by an important z
p p g y person is more prestigious than chosen by a less
important person.
For example, if a company CEO votes for a person is |
much more important than a worker votes for the person.
If one’s circle of influence is full of prestigious actors, z
then one’s own prestige is also high.
Thus one’s prestige is affected by the ranks or statuses of |
thth i l d t e involved actors.
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
4545ﻫﻢﻫﻢ اﺳﺘﻨﺎدي اﺳﺘﻨﺎدي وو زوج زوج ﻛﺘﺎﺑﺸﻨﺎﺧﺘﻲ ﻛﺘﺎﺑﺸﻨﺎﺧﺘﻲ Coupling Coupling
Another Another area of research concerned with links is area of research concerned with links is z
citation analysis of scholarly publications.
A scholarly p y publication cites related prior work to |
acknowledge the origins of some ideas and to compare
the new proposal with existing work.
When a paper cites another paper, a relationship is z
established between the publications.
Citation analysis uses these relationships (links) to perform |
various types of analysis.
We We discuss two types of citation analysis discuss two types of citation analysis, coco- z
citation and bibliographic coupling. The HITS
algorithm algorithm is related to these two types of analysis is related to these two types of analysis.
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
4646ﻫﻢﻫﻢ اﺳﺘﻨﺎدي اﺳﺘﻨﺎدي CoCo-citationupling citationupling
IfIf papers papers ii and and jj are are both cited by paper both cited by paper kk,, then they then they zz
may be related in some sense to one another.
The The more papers they are cited by the stronger more papers they are cited by, the stronger z
their relationship is.
Let L be the citation matrix. Each cell of the matrix is z
defined defined as follows: as follows:
Lij
= 1 if paper i cites paper j, and 0 otherwise. |
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
4747Bibliographic Bibliographic Coupling Coupling ﻛﺘﺎﺑﺸﻨﺎﺧﺘﻲ زوج
Bibliog p p g p graphic coupling operates on a similar z
principle.
Bibliographic coupling links papers that cite the z
same articles
if papers i and j both cite paper k, they may be related. |
The more papers thth b th it th t th i ey both cite, the stronger their z
similarity is.
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
4848Bibliographic Bibliographic Coupling Coupling ﻛﺘﺎﺑﺸﻨﺎﺧﺘﻲ زوج
Bibliog p p g p graphic coupling operates on a similar z
principle.
Bibliographic coupling links papers that cite the z
same articles
if papers i and j both cite paper k, they may be related. |
The more papers thth b th it th t th i ey both cite, the stronger their z
similarity is.
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
4949ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﻜﻪ ﺷﺒﻜﻪ ﻫﺎي ﻫﺎي اﺟﺘﻤﺎﻋﻲ
z ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﻜﻪ اﺟﺘﻤﺎﻋﻲ ( social network analysis)، روﻳﻜﺮد ﭘﮋوﻫﺸﻲ اﺳﺖ
ﻛﻪﻛﻪ يﺑﻪﻪ اﻟﮕﻮ اﻟﮕ ﻫﺎﻫﺎ رواﺑا ﻂﻂ ﺑﻴﻦﻦ اﻓﺮ اﻓ اد اد، ﮔﮔﺮوهﻫﺎﻫﺎ و ﺳﺎزﻣﺎن ﺎز ﺎنﻫﺎﻫﺎ ﻣﻲﭘﺮدازد دازد و اﺑا ﺘﺪا ﺘﺪا ددر
ﺟﺎﻣﻌﻪﺷﻨﺎﺳﻲ، رواﻧﺸﻨﺎﺳﻲ اﺟﺘﻤﺎﻋﻲ و ﻋﻠﻮم ارﺗﺒﺎﻃﺎت ﺷﻜﻞ ﮔﺮﻓﺖ .
z داﻧﺸﻤﻨﺪانن ﺣﻮزﻮزه وب وبﺳﻨﺠﻲﺠﻲ ازز داﻳﻦ ﻳﻦ روﻳﻜﺮ روﻳ ﺮ درر ﻣﻄﺎﻟﻌﺎت ﺣﻮزﻮزه وب وب اﺳﺘﻔﺎده ﻛﺮﺮدهاﻧﺪ وو
ﺑﻪ ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﻜﻪﻫﺎي اﺟﺘﻤﺎﻋﻲ ﻣﺤﻴﻂ ﭘﻴﻮﺳﺘﻪ ﭘﺮداﺧﺘﻪاﻧﺪ.
z آﻧﻬﺎ ﻣﻌﺘﻘﺪﻧﺪ، ﺷﺒﻜﻪﻫﺎي راﻳﺎﻧﻪاي ﻧﻴﺰ ﺑﻪ دﻟﻴﻞ اﻳﻨﻜﻪ ﻣﻲﺗﻮاﻧﻨﺪ اﻓﺮاد و ﺳﺎزﻣﺎنﻫﺎ را ﺑﺎ
ﻫﻢ ﻣﺮﺗﺒﻂﻂ ﻛﻛﻨﻨﺪ، اﻣ ا ﻜﺎﻜﺎن ااﻳﻦ راا ﻪداارﻧﺪ ﻛﻛ ﺑﺮ اﺳ ا ﺎﺎس ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻠ ﻞﻞﻫﺎﺎي ﺷﺒﻜﻜﻪ اﺟﺘﻤ ا ﺎﺎﻋﻲ ﻣﻮرد
ﻣﻄﺎﻟﻌﻪ ﻗﺮار ﺑﮕﻴﺮﻧﺪ
zz ارﺗﺒ ا ﺗ ﺎﻃﺎت ﺎﻃﺎت اﻓﺮ اﻓ اد اد ددر ﻣﺤﻴ ﻣﺤ ﻂﻂ ﺷﺒﺷ ﻜﻪﻜﻪ و ﻣﺸﺨﺼﺎ ﻣﺸﺨﺼﺎ وبب، ﺑﻪ ﺑﻪ دﻻﻳﻞ دﻻﻳﻞ و اﺷﻜﺎل اﺷﻜﺎل ﮔﻮﻧﺎﮔﻮ ﮔ ﻧﺎﮔ ﻧﻧﻲ اﺗﻔﺎق اﺗﻔﺎق
ﻣﻲاﻓﺘﺪ.
z ﺑﺮاي ﻣﺜﺎل، ﺷﺒﻜﻪﻫﺎي ﻣﻮﺿﻮﻋﻲ، ﻋﻠﻤﻲ، ﺻﻨﻔﻲ، ورزﺷﻲ، ﺳﻴﺎﺳﻲ، وﻃﻦﭘﺮﺳﺘﻲ و
ﺑﺴﻴﺎري ﺑ ﻴ ري اﻧﻮاع ﻮ ع ﺷﺒﻜﻪﻫﺎي ﺒ ي اﺟﺘﻤﺎﻋﻲ ﺟ ﻲ دﻳﮕﺮ ﻳ ﺮ ﻂدرر ﻣﺤﻴﻴ ﻣﺠﺎزي ﺠ زي ﺷﻜﻞﻞ ﮔﺮﺮﻓﺘﻪ وو ﻫﺮﺮ روز روز ﻫﻢﻢ
ﮔﺴﺘﺮش ﺑﻴﺸﺘﺮي ﻣﻲﻳﺎﺑﺪ.
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
5050ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﻜﻪ ﺷﺒﻜﻪ ﻫﺎي ﻫﺎي ارﺗﺒﺎﻃﺎت ارﺗﺒﺎﻃﺎت ﻋﻠﻤﻲ ﻋﻠﻤﻲ
z وب، ﺑﺴﻴﺎري از روشﻫﺎي ﭘﮋوﻫﺸﮕﺮان ﺑﺮاي دﺳﺘﺮﺳﻲ ﺑﻪ ﻣﻨﺎﺑﻊ ﻋﻠﻤﻲ، ﺷﻴﻮه اﻧﺠﺎم
ﭘﮋوﮋ ﻫﺶ ﻫﺶ، ﺗﺒﺗ ﺎدل ﺎدل و اﻧﺘﺸﺎ اﻧﺘﺸﺎر ﻳﺎﻓﺘﻪ ﺎﻓﺘﻪﻫﺎﻫﺎ و ﺑﻪﻪ ﻃﻃﻮر ﻛﻠﻛﻠﻲ ﻓﻌﺎﻟﻴﺖ ﻓ ﺎﻟ ﺖﻫﺎﻫﺎي ﻋﻠﻋﻠﻤﻲ راا ﺗﻐﺗﻐﻴﻴﺮ دادداده اﺳ ا ﺖﺖ.
z ﺑﻪ ﻫﻤﻴﻦ دﻟﻴﻞ، اﻛﻨﻮن ﺿﺮورﺗﻲ ﺑﺮاي ارزﻳﺎﺑﻲ ﺗﺎﺛﻴﺮ وب در رﻓﺘﺎرﻫﺎي ﻋﻠﻤﻲ ﺑﻪ وﺟﻮد
آﻣﺪه اﺳﺖ
z در ﻣﻄﺎﻟﻌﺎﺗﻲ ﻛﻪ ﺑﺎ ﻫﺪف ﺳﻨﺠﺶ ارﺗﺒﺎﻃﺎت ﻋﻠﻤﻲ ( scholarly
communications) ﺻﻮرت ﮔﺮﻓﺘﻪ اﺳﺖ، ﺳﺎﻳﺖ ﻣﺠﻼت و داﻧﺸﮕﺎهﻫﺎ ﺑﻴﺶ از
ﺳﺎﻳﺮ ﺳﺎﻳﺖﻫﺎ ﻣﻮرد ﺗﻮﺟﻪ ﭘﮋوﻫﺸﮕﺮان وبﺳﻨﺠﻲ ﺑﻮده اﺳﺖ.
z ﺑﻪﻃﻮر ﻛﻠﻲ، ﻧﺘﺎﻳﺞ ﻣﻄﺎﻟﻌﺎت ﺑﻪوﻳﮋه در ﺳﺎلﻫﺎي اﺧﻴﺮ ﻧﺸﺎن ﻣﻲدﻫﺪ ﻛﻪ ﻣﻴﺎن ﭘﻴﻮﻧﺪ ﺑﻪ
ﺳﺎﻳﺖ ﺳﺎﻳﺖ ﻣﺠﻼت ﻣﺠﻼت ﻋﻠﻤ ﻋﻠﻤﻲ وو ﺗﻌﺪاد ﺗﻌﺪاد اﺳﺘﻨﺎد اﺳﺘﻨﺎد ﺑﻪ ﺑﻪ آﻧﻬﺎ آﻧﻬﺎ دردر ﭘﺎﻳﮕﺎه ﭘﺎﻳﮕﺎه آي آي.اس اس.آي آي. ارﺗﺒﺎط ارﺗﺒﺎط ﻣﻌﻨ ﻣﻌﻨﻲداردار
ﻣﺴﺘﻘﻴﻤﻲ وﺟﻮد دارد.
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
5151ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﭘﻴﻮﻧﺪﻫﺎي ﭘﻴﻮﻧﺪﻫﺎي وﺑﻲ وﺑﻲ
z ﻣﻬﻤﺘﺮﻳﻦ ﻣﺒﺤﺚ ﻣﻄﺮح در ﻣﻄﺎﻟﻌﺎت وبﺳﻨﺠﻲ، ﻣﻄﺎﻟﻌﻪ ﺑﺮ روي ﭘﻴﻮﻧﺪﻫﺎ ﻳﺎ ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ
.ااﺳﺖ (lili knk anall i ysis) ﭘﻴﻮﻧﺪ
z ﭘﻴﻮﻧﺪﻫﺎ ﺑﻪ ﻋﻨﻮان ﭘﻞﻫﺎي ارﺗﺒﺎﻃﻲ ﺑﻴﻦ ﺳﺎﻳﺖﻫﺎي وﺑﻲ، ﺗﻌﻴﻴﻦﻛﻨﻨﺪه وﺿﻌﻴﺖ
وبﺳﺎﻳﺎ ﺖﺖﻫﺎﻫﺎ از از ﻧﻈ ﻧﻈﺮ ﻣﺤﺘﻮﺘ اا، ارﺗﺒ ا ﺗ ﺎﻃﺎت ﺎﻃﺎت وﻣﻮﺿﺿﻮﻋﻲ اﻫﻤﻴ اﻫ ﺖﺖ ﻫﺴ ﻫ ﺘﻨﺪ ﺘﻨﺪ.
z اﻫﻤﻴﺖ ﭘﻴﻮﻧﺪﻫﺎ در ﻣﺤﻴﻂ وب ﺑﻪ ﺣﺪي اﺳﺖ ﻛﻪ ﺣﻮزهﻫﺎي ﺗﺨﺼﺼﻲ وﻳﮋهاي ﺑﺮاي
ﻣﻄﺎﻟﻌﺎت ﻣﻄﺎﻟﻌﺎت ﭘﻴﻮﻧﺪي ﭘﻴﻮﻧﺪي ددر اﻳﻦ اﻳﻦ ﻣﺤﻴﻂ ﻣﺤﻴﻂ ﭼﻮن ﭼﻮن ﻣﻄﺎﻟﻌﻪ ﻣﻄﺎﻟﻌﻪ اﻧﮕﻴﺰه اﻧﮕﻴﺰهﻫﺎي ﻫﺎي ﭘﻴﻮﻧﺪ، ﭘﻴﻮﻧﺪ، ﻣﻄﺎﻟﻌﺎت ﻣﻄﺎﻟﻌﺎت ﻛﻤﻛﻤﻲ ﺑﺑﺮ روي وي
ﭘﻴﻮﻧﺪﻫﺎ و ﺑﺮرﺳﻲ ﻧﻘﺶ ﭘﻴﻮﻧﺪﻫﺎ در ارﺗﺒﺎﻃﺎت ﻋﻠﻤﻲ ﺑﻪ وﺟﻮد آﻣﺪه اﺳﺖ.
zz ﺗﺤﻠﻴ ﺗﺤﻠ ﻞﻞ ﭘﻴﻮﻧﺪ ﻧﺪ، ﻃﺒﻃ ﻖﻖ ﺗﻌﺮﻳ ﺗ ﻒﻒ وﻳﻜﻜﻲﭘﺪﻳﺪ ﺎﺎ ((2008 2008)) ﻋﺒﺎر ﻋ ﺎ تت اﺳ ا ﺖﺖ از از::
|“زﻳﺮ ﻣﺠﻤﻮﻋﻪاي از ﺷﺒﻜﻪﺳﻨﺠﻲ ﺑﻪﻛﻪ ﻛﺸﻒ ﺑﻴﻦرواﺑﻂ
ﻣﻮﺟﻮ ﻮ ﻮدﻳﺖﻫﺎ دﻣﻲﻲﭘﺮداز ﭘﺮ ز . ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞﻞ ﭘﻴﻮ ﭘ ﻮﻧﺪ درر ﻣﺤﻴﻂ ووب، ﺑﻪ ﻣﻄﺎﻟﻌﻪ
ارﺗﺒﺎﻃﺎت ﻣﻮﺟﻮد ﺑﻴﻦ ﺗﻜﻪﻫﺎي اﻃﻼﻋﺎﺗﻲ ﻣﻲﭘﺮدازد ﻛﻪ ﻧﻤﻲﺗﻮاﻧﻨﺪ
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ ﻣﺠﺰا از ﻳﻜﺪﻳﮕﺮ ﺑﻪ ﻫﺪف ﺧﻮد دﺳﺖ ﭘﻴﺪا ﻛﻨﻨﺪ”.
5252ﭘﻴﻮﻧﺪﺷﻤﺎري
z ﺑﺮاي ﻣﺤﺎﺳﺒﻪ ﻣﻴﺰان ﭘﻴﻮﻧﺪﻫﺎ از ﻣﻮﺗﻮرﻫﺎي ﻛﺎوش اﺳﺘﻔﺎده ﻣﻲ ﺷﻮد
z ﺑﺴﺘﻪ ﺑﻪ ﻧﻮع ﭘﮋوﻫﺶ، ﻣﻮﺗﻮر ﻛﺎوش اﻧﺘﺨﺎﺑﻲ ﻣﻤﻜﻦ اﺳﺖ ﻣﺘﻔﺎوت ﺑﺎﺷﺪ.
z در ﺣﺎل ﺣﺎﺿﺮ ﺑﻬﺘﺮﻳﻦ ﻣﻮﺗﻮرﻫﺎي ﻛﺎوش ﺑﺮاي ﻣﺤﺎﺳﺒﻪ ﭘﻴﻮﻧﺪﻫﺎ، ﻳﺎﻫﻮ و آﻟﺘﺎوﻳﺴﺘﺎ ( اﻟﺒﺘﻪ
ااﻳﻦ ﻣﻮﺗﻮر ﻧﻴﺰ ﺗﻮﺳﻂﻂ ﻳﺎﺎﻫﻮ ﻣﺪﻳﺮﻳﺖ ﻣﻲ ﺷﻮد) و درﺟﻪدر ﺑﻌﺪي، ﮔﻮﮔ ﮔﻞ ﮔﻞ ﻫﺴﺘﻨﺪ.
z ﺑﺮاي ﻣﺤﺎﺳﺒﻪ ﭘﻴﻮﻧﺪﻫﺎ در ﻫﺮ ﻳﻚ از اﻳﻦ ﻣﻮﺗﻮرﻫﺎ ﺑﺎﻳﺪ ﻓﺮﻣﻮل ﺧﺎص آﻧﻬﺎ را ﺑﻪ ﻛﺎر ﺑﺮد.
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
5353ﭘﻴﻮﻧﺪﻫﺎ
،(out-link ) ﺑﻴﺮوﻧﻲ ﭘﻴﻮﻧﺪ z
،(in-link) درﻳﺎﻓﺘﻲ ﭘﻴﻮﻧﺪ z
،(self-Link ) ﭘﻴﻮﻧﺪي ﺧﻮد z
،(co-link) ﭘﻴﻮﻧﺪي-ﻫﻢ z
(total- Links) ﭘﻴﻮﻧﺪﻫﺎ ﻣﺠﻤﻮع z
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
5454ﭘﻴﻮﻧﺪ ﻫﺎي ﺑﻴﺮوﻧﻲ
z ﺑﻪ ﭘﻴﻮﻧﺪﻫﺎﺋﻲ ﮔﻔﺘﻪ ﻣﻲﺷﻮد ﻛﻪ از ﻳﻚ ﺻﻔﺤﻪ وب ﻣﻮﺟﻮد در ﻳﻚ ﺳﺎﻳﺖ ﺑﻪ ﺻﻔﺤﻪ وب
ﻣﻮﺟﻮد در ﺳﺎﻳﺖ دﻳﮕﺮي داده ﻣﻲﺷﻮد و در واﻗﻊ ﻣﻌﺎدل واژه"ارﺟﺎع" در آﺛﺎر ﭼﺎﭘﻲ
اﺳ ا ﺖﺖ.
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
5555ﭘﻴﻮﻧﺪ ﭘﻴﻮﻧﺪ ﻫﺎي ﻫﺎي دروﻧﻲ دروﻧﻲ ((ﺑﻪ ﺑﻪ ﺧﻮد ﺧﻮد))
z ﺑﻪ ﭘﻴﻮﻧﺪﻫﺎﺋﻲ ﮔﻔﺘﻪ ﻣﻲ ﺷﻮد ﻛﻪ ﻳﻚ ﺻﻔﺤﻪ وب در ﻳﻚ ﺳﺎﻳﺖ ﺑﻪ ﻫﻤﺎن ﺻﻔﺤﻪ و ﻳﺎ
ﺮﺻﻔﺤﻪ ﻔ ﻪﻫﺎﻫﺎي دﻳد ﮕﮕ ﻣﻮﺟﻮدد ددر ﻫﻤﻫ ﺎن ﺎن رﺳﺎﻳﺎ ﺖﺖ ﻣﻲﺑﺮﻗﺮﻗ اا ﻛﻨﺪ ﻛﻨﺪ.
z ﺧﻮدﭘﻴﻮﻧﺪيﻫﺎ، ﺳﺎﺧﺘﺎري ﻣﻨﻄﻘﻲ را ﺑﺮاي ﺳﺎزﻣﺎﻧﺪﻫﻲ ﺻﻔﺤﺎت وب در ﺳﺮورﻫﺎي
ﻣﺤﻠﻲﻲ اﻧﻌﻜﺎسس ﻣﻲﻲدﻫﻨﺪ ((اﻳﻨﮕﻮرﺳﻦ ﻳ ﻮر ﻦ، 1998)).
z ﻫﺮ ﭼﻪ ﻣﻴﺰان ﺧﻮدﭘﻴﻮﻧﺪيﻫﺎي ﻳﻚ وبﺳﺎﻳﺖ ﺑﻴﺸﺘﺮ ﺑﺎﺷﺪ، ﻧﺸﺎﻧﮕﺮ اﻳﻦ اﺳﺖ ﻛﻪ
ّ اﻃﻼﻋﺎت و ﺻﻔﺤﺎت درون وبﺳﺎﻳﺖ ﺑﻪ ﺧﻮﺑﻲ ﺑﻪ ﻫﻢ رﺑﻂ داده ﺷﺪهاﻧﺪ
z ﻫﺮ ﭼﻪ ﺧﻮدﭘﻴﻮﻧﺪﻫﺎي ﻳﻚ وبﺳﺎﻳﺖ ﺑﻴﺸﺘﺮ ﺑﺎﺷﺪ، ّ اﻃﻼﻋﺎت و ﺻﻔﺤﺎت آن، ﺑﻴﺸﺘﺮ و
ﺑﻬﺘﺮ ﺑﻪ ﻣﻮﺗﻮرﻫﺎي ﻛﺎوش ّ ﻣﻌﺮﻓﻲ ﺷﺪه و ﻧﻤﺎﻳﻪ ﻣﻲﺷﻮﻧﺪ و در ﻧﺘﻴﺠﻪ ﻣﺤﺘﻮﻳﺎت وبﺳﺎﻳﺖ
ﺑﻬﺘﺮ ﺑﺎزﻳﺎﺑ ﺑﺎزﻳﺎﺑﻲ ﻣﻣﻲﺷﻮد ﺷﻮد .
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
5656ﭘﻴﻮﻧﺪ ﭘﻴﻮﻧﺪ ﻫﺎي ﻫﺎي درﻳﺎﻓﺘﻲ
z ﻣﻬﻤﺘﺮﻳﻦ و ارزﺷﻤﻨﺪﺗﺮﻳﻦ ﻧﻮع ﭘﻴﻮﻧﺪ
z ﺑﻪ ﭘﻴﻮﻧﺪﻫﺎﺋﻲ ﺷﻮدﮔﻔﺘﻪ ﻣﻲ ﻛﻪ ﻳﻚ ﺻﻔﺤﻪ وب از ﺳﺎﻳﺮ ﺻﻔﺤﻪﻫﺎي درﻳﺎﻓﺖوب
ﻣﻲﻛﻨﺪ .
z اﻳﻦ ﻣﻔﻬﻮم ﻣﻌﺎدل واژه""اﺳﺘﻨﺎد"" در آآﺛﺎر ﭼﺎﭘﻲ اﺳﺖ.
z ﺑﻪ ﭘﻴﻮﻧﺪﻫﺎﻳﻲ ﻛﻪ ﺑﻪ ﻳﻚ ﺳﺎﻳﺖ داده ﻣﻲ ﺷﻮد ﮔﻔﺘﻪ ﻣﻲ ﺷﻮد.
z ﻣﻲﺗﻮان ﮔﻔﺖ ﻛﻪ ﻫﺮ ﭼﻪ ﭘﻴﻮﻧﺪﻫﺎي درﻳﺎﻓﺘﻲ ﻳﻚ وبﺳﺎﻳﺖ ﺑﻴﺸﺘﺮ ﺑﺎﺷﺪ ﻧﺸﺎن دﻫﻨﺪه
اﻳﻦ اﺳﺖ ﻛﻪ در آن وبﺳﺎﻳﺖ ّ اﻃﻼﻋﺎت ﻣﻔﻴﺪي وﺟﻮد دارد ﻛﻪ ﻛﺎرﺑﺮان ﺑﻪ آﻧﻬﺎ ﻧﻴﺎز
داﺷﺘﻪ داﺷﺘﻪ و آﻧﻬﺎ آﻧﻬﺎ ﺮراا ﺑﻴﺑ ﺸﺘﺸﺘ ﻣﻮر ﻣ دد اﺳﺘﻔﺎده اﺳﺘﻔﺎده ﻗﺮﻗ اار ﻣﻣﻲدﻫﻨﺪ دﻫﻨﺪ.
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
5757ﻫﻢ ﭘﻴﻮﻧﺪي
z ﻫﻢﭘﻴﻮﻧﺪي ﺑﻪ اﻳﻦ ﻣﻌﻨﺎ اﺳﺖ ﻛﻪ ﭘﻴﻮﻧﺪ دو وبﺳﺎﻳﺖ در ﻛﻨﺎر ﻫﻢ و در ﺳﺎﻳﺖ ﺳﻮﻣﻲ
ﻇﺎﻫﺮ ﺷﻮد.
z اﻳﻦ وﺿﻌﻴﺖ ﻣﺸﺎﺑﻪ ﺣﺎﻟﺖ ﻫﻢ اﺳﺘﻨﺎدي در ﻣﻨﺎﺑﻊ ﭼﺎﭘﻲ اﺳﺖ .
z وﻗﺘﻲ دو ﻧﻮﺷﺘﻪ ﻳﺎﺎ وبﺳﺎﺎﻳﺖ ﺑﺎﺎ ﻳﻜﺪﻳﮕﮕﺮ ﻫﻢاﺳﺘﻨ ا ﺎﺎدي ﻳﺎﺎ ﻫﻢﭘﻴﻮﻧﺪي دااﺷﺘﻪ زﺑﺎﺎﺷﻨﺪ اا ااﻳﻦ
ﺟﻬﺖ ﺣﺎﺋﺰ اﻫﻤﻴﺖ اﺳﺖ ﻛﻪ ﻧﺸﺎﻧﮕﺮ ﻧﻮﻋﻲ راﺑﻄﻪ ﺑﻴﻦ آﻧﻬﺎ ﺑﺎ ﻳﻜﺪﻳﮕﺮ اﺳﺖ.
zz ﺑﻪ ﻋﺒﺎرﺎ تت دﻳﮕﮕﺮ، آﻧﻬ آﻧ ﺎﺎ اﺷﺘﺮ اﺷﺘ اﻛ اﻛﻲ در ﺣﻮزه ﻛﺎﻛﺎري، روشﻫش ﺎﺎي ﻣﻮرد اﺳ ا ﺘﻔﺎ ﺘﻔﺎده و اﻃﻼﻋ اﻃﻼ ﺎت ﺎت ﻣﻮرد
ﻋﻼﻗﻪ دارﻧﺪ ﻛﻪ ﺑﺎﻋﺚ ﺷﺪه اﺳﺖ اﻳﻦ دو در ﻛﻨﺎر ﻫﻢ در ﺳﺎﻳﺖ دﻳﮕﺮي ﻇﺎﻫﺮ ﺷﻮﻧﺪ .
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
5858ﻣﺠﻤﻮع ﭘﻴﻮﻧﺪﻫﺎ
z ﻣﺠﻤﻮع ﭘﻴﻮﻧﺪﻫﺎ ﻛﻪ ﺷﺎﻣﻞ ﺗﻤﺎﻣﻲ ﭘﻴﻮﻧﺪﻫﺎي درﻳﺎﻓﺘﻲ ( دروﻧﻲ ) و ﺧﻮدﭘﻴﻮﻧﺪﻫﺎي ﻳﻚ
ﺳﺎﺎﻳﺖ ﻣﻲﺷﻮد، ﻧﺸﺎﺎن ﻣﻲدﻫﺪ ﻛﻛﻪ وﺿﻌﻴﺖ آآن زﺳﺎﺎﻳﺖ اا ﻟﺤ ﻟ ﺎظ ﺎظ درﻳﺎﻓﺎﻓﺖ ﭘﻴﻮﻧﺪ ﭼﮕﮕﻮﻧﻪ
اﺳﺖ.
zz ﺑﺮرﺳﻲ و ﻣﻄﺎﻟﻌ ﻄﺎﻟ ﻪﻪ ﻣﺠﻤﻮعع ﭘﻴﻮﻧﺪ ﻧﺪ وﺳﺎﻳﺖ ﺎ ﺖﻫﺎﻫﺎ ﺳﭙﺲ ﻣﻄﺎﻟﻌ ﻄﺎﻟ ﻪﻪ ﺟﺪاﮔﺎﻧﻪ ﺪاﮔﺎﻧﻪ ﭘﻴﻮﻧﺪﻫﺎ ﻧﺪﻫﺎي درﻳد ﺎﻓﺘ ﺎﻓﺘﻲ و
ﺧﻮدﭘﻴﻮﻧﺪيﻫﺎ، ﻧﺘﺎﻳﺠﻲ در ﺧﺼﻮص وﺿﻌﻴﺖ ﺣﻀﻮر ﺳﺎﻳﺖ در ﻣﺤﻴﻂ وب و اﻋﺘﺒﺎر
ﭘﻴﻮﻧﺪﻫﺎي ﭘﻴﻮ ي ﻪآنن ﺑﺑ دﺳﺖ ﻣﻲﻲدﻫﺪ.
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
5959ﺿﺮﻳﺐ ﺗﺎﺛﻴﺮ ﺿﺮﻳﺐ ﺗﺎﺛﻴﺮ وب
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
6060ﻣﺠﻤﻮع ﭘﻴﻮﻧﺪﻫﺎ
z ﺿﺮﻳﺐ ﺗﺎﺛﻴﺮﮔﺬار ﺧﺎرﺟﻲ
z ﺿﺮﻳﺐ ﺗﺎﺛﻴﺮﮔﺬار داﺧﻠﻲ
z ﺿﺮﻳﺐ ﺗﺎﺛﻴﺮﮔﺬار ﻛﻠﻲ
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
6161ﺿﺮﻳﺐ ﺗﺎﺛﻴﺮ ﺿﺮﻳﺐ ﺗﺎﺛﻴﺮ داﺧﻠﻲ
self-link WIF (Web داﺧﻠﻲ ﺗﺎﺛﻴﺮﮔﺬار ﻋﺎﻣﻞ z
(impact impact factor) factor،، ﺑﺮاﺳﺎس ﺑﺮاﺳﺎس ﻧﺴﺒﺖ ﻧﺴﺒﺖ ﺗﻌﺪاد ﺗﻌﺪاد ﭘﻴﻮﻧﺪﻫﺎي ﭘﻴﻮﻧﺪﻫﺎي
ﺻﻮرت ﮔﺮﻓﺘﻪ در درون ﺳﺎﻳﺖ ﻧﺴﺒﺖ ﺑﻪ ﻛﻞ ﺻﻔﺤﺎت
ﻧﻤ ﻧ ﺎﻳﻪ ﺎﻳﻪﺳﺎزي ﺳﺎزي ﺷﺪه ﺷﺪه ﺳﺎﻳﺖ ﺳﺎﻳﺖ ددر ﻣﻮﺗﻮ ﻣﻮﺗﻮر ﻛﺎوش ﻛﺎوش ﻣﻮر ﻣﻮ دد اﺳﺘﻔﺎده اﺳﺘﻔﺎده ﺑﻪ ﺑﻪ
دﺳﺖ ﻣﻲآﻳﺪ.
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
6262ﺿﺮﻳﺐ ﺗﺎﺛﻴﺮ ﺿﺮﻳﺐ ﺗﺎﺛﻴﺮ ﺧﺎرﺟﻲ
inin link link WIF WIF (Web (Web ﺧﺎﺧﺎرﺟﻲ ﮔﺬا ﮔﺬا ﺎﺛ ﺗﺎﺛﻴﺮ ﻞﻞ رﻋﺎﻣﺎ zz
(impact factor ﻛﻪ ﺑﺎ ﻋﻨﻮان ﻋﺎﻣﻞ ﺗﺎﺛﻴﺮﮔﺬار
ﺗﺠﺪﻳﺪﻧﻈﻈﺮ ﺷﺪه ﺺﻳﺎﺎ ﺧﺎﻟﺎﻟ ﻧﻴﺰ ااز آآن ﻳﺎﺎد ﻣﻲﺷﻮد، ﺑﻪ
ﺑﺮرﺳﻲ ﭘﻴﻮﻧﺪﻫﺎﻳﻲ ﻛﻪ از ﺧﺎرج ﺑﻪ وبﺳﺎﻳﺖ ﻣﻮرد ﻧﻈﺮ
ﺑﺮﻗﺮار ﻣﻲﺷﻮﻧﺪ ﻣﻲﭘﺮدازد
z ﺑﺮاي ﺑﺮ ي ﻣﺤﺎﺳﺒﺒﻪ ﻋﺎﻣﻞﻞ ﺗﺎﺛﻴﺮﮔﺬاري ﻴﺮ ري ﺗﺠﺪﻳ ﺠ ﻳﺪ ﻧﻈﺮﺮ ﺷﺪه
وبﺳﺎﻳﺖﻫﺎ از ﻓﺮﻣﻮل زﻳﺮ اﺳﺘﻔﺎده ﻣﻲﺷﻮد:
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
6363ﺿﺮﻳﺐ ﺗﺎﺛﻴﺮ ﺿﺮﻳﺐ ﺗﺎﺛﻴﺮ ﻛﻠﻲ
overallll (t(t t l) otal) WIF WIF (W(W beb ﻛﻠﻲ ﺗﺎﺛﻴﺮﮔﺬاري ﺿﺮﻳﺐ ﺑﺎ z
(impact factor، ﺑﻪ ﻣﺤﺎﺳﺒﻪ ﺗﻤﺎﻣﻲ ﭘﻴﻮﻧﺪﻫﺎﻳﻲ ﻛﻪ ﻣﻤﻜﻦ
اﺳﺖ وب ﺳﺎﻳﺖ درﻳﺎﻓﺖ ﻛﺮده ﺑﺎﺷﺪ ﭘﺮداﺧﺘﻪ ﻣﻲﺷﻮد ﺗﺎ ﻣﺸﺨﺺ
ﺷﻮد ﻛﻪ وﺿﻌﻴﺖ ﺳﺎﻳﺖ از ﻧﻈﺮ ﭘﭘﻴﻮﻧﺪي ﺑﻪ ﻃﻮر ﻛﻠﻲﻲ ﭼﮕﻮﻧﻪ اﺳﺖ و
ﭼﻪ ﺟﺎﻳﮕﺎﻫﻲ دارد. ﺑﺮاي ﻣﺤﺎﺳﺒﻪ ﺿﺮﻳﺐ ﺗﺎﺛﻴﺮﮔﺬار ﻛﻠﻲ ﺳﺎﻳﺖ،
ﺗﻤﺎﻣﻲﻲ ﭘﻴﻮﻧﺪﻫﺎي ﭘﻴﻮ ي درﻳﺎﻓﺘﻲ رﻳ ﻲ وو اﺧﻮدﭘﻴﻮﻧﺪي ﻮ ﭘﻴﻮ يﻫﺎ رر ﺑﺮ ﺑﺮ ﺗﻤﺎﻣﻲﻲ ﺻﻔﺤﺎت
وبﺳﺎﻳﺖ ﻛﻪ در ﻣﻮﺗﻮر ﻛﺎوش ﻣﻮرد اﺳﺘﻔﺎده ﻧﻤﺎﻳﻪ ﺷﺪه اﺳﺖ،
ﺗﻘﺴﻴﻢ ﻣﻣﻲﻛﻨﻨﺪ .
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
6464ﺿﺮﻳﺐ ﺗﺎﺛﻴﺮ ﺿﺮﻳﺐ ﺗﺎﺛﻴﺮ ﻛﻠﻲ
z روﺷﻲ ﻛﻪ ﺑﺮاي ﻣﺤﺎﺳﺒﻪ وبﺳﺎﻳﺖﻫﺎي ﭘﻴﺸﻨﻬﺎدﻫﺴﺘﻪ ﺷﺪه
اﺳﺖ ﺑﺮﺮ اﺳﺎسس ﻓﺮﻣﻮ ﺮ ﻮل زﻳﺮ ز ﺮ وو ﻣﻴﺰان ﺰ ن ﭘﻴﻮ ﭘ ﻮﻧﺪﻫﺎي درﻳﺎﻓﺘﻲ ر ﻲ
ﺳﺎﻳﺖﻫﺎي ﻳﻚ ﻣﻮﺿﻮع ﻳﺎ زﻣﻴﻨﻪ وﻳﮋه اﺳﺖ:
CC zz == ﺷﺎﺧﺺ ﺷﺎﺧﺺ ﺗﻌﻴﻴ ﺗﻌ ﻦﻦ وب وب ﺳﺎﻳﺖ ﺳﺎﻳﺖ ﻫﺎي ﻫﺎي ﻫﺴ ﻫ ﺘﻪ ﺘﻪ
t z = ﻣﺠﻤﻮع ﭘﻴﻮﻧﺪﻫﺎي درﻳﺎﻓﺘﻲ ﺗﻮﺳﻂ وب ﺳﺎﻳﺖﻫﺎي ﻣﻮرد
ﻣﻄﺎﻟﻌﻪ
n z= ﺗﻌﺪاد ووبﺳﺎﻳﺖﻫﺎي ﻣﻮرد ﻣﻄﺎﻟﻌﻪ
z C=t/n
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
6565ﭼﺎﻟﺶ ﭼﺎﻟﺶﻫﺎي ﻫﺎي وب وب ﺳﻨﺠﻲ
z ﻧﺎﭘﺎﻳﺪاري ﭘ ﻳ ري ﺻﻔﺤﺎت وب
z اﺷﻜﺎﻻت وارد ﺑﺮ ﭘﻴﻮﻧﺪ و اﺳﺘﻨﺎد
z ﻣﺴﺎﺋﻞ زﺑز ﺎﻧﺎﻧﻲ
z ﻣﺴﺎﺋﻞ ﻣﻮﺗﻮرﻫﺎي ﺑﻪﻛﺎوش ﻋﻨﻮان اﺑﺰارﻫﺎي ﮔﺮدآوري
اﻃﻼﻋﺎت
z ﻋﺪم ﻋﺪم ﺷﻨﺎﺳﺎﻳﻲ ﺷﻨﺎﺳﺎﻳﻲ ﭘﻴﻮﻧﺪﻫﺎي ﭘﻴﻮﻧﺪﻫﺎي ﻣﻮﺟﻮد ﻣﻮﺟﻮد دردر ﺻﻔﺤﺎﺗﻲ ﺻﻔﺤﺎﺗﻲ اﺳﺖ اﺳﺖ ﻛﻪﻛﻪ ﺑﺎﺑﺎ اﺳﺘﻔﺎده اﺳﺘﻔﺎده
از زﺑﺎن ﺑﺮﻧﺎﻣﻪﻧﻮﻳﺴﻲ ﺟﺎوا ﻃﺮاﺣﻲ ﺷﺪه-اﻧﺪ Java Script
zz ﻋﺪم دﺳﺘﺘﺮﺳﻲ ﺑﻪ اﻃﻼﻋ اﻃﻼ ﺎﺗﺎﺗﻲ ﻛﻛﻪ در يﭘﺎﻳﺎ ﮕﺎﮕﺎه ﻲﻫﺎﺎ اﻃﻼﻋ اﻃﻼ ﺎﺗﺎﺗ درج
ﺷﺪه و ﻧﻴﺎز ﺑﻪ رﻣﺰ ﻋﺒﻮر دارﻧﺪ
z ﻧﺎﻣﺮﺋﻲوب
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
6666ﭼﺎﻟﺶ ﭼﺎﻟﺶﻫﺎي ﻫﺎي وب وب ﺳﻨﺠﻲ
z ﻧﺎﭘﺎﻳﺪاري ﭘ ﻳ ري ﺻﻔﺤﺎت وب
z اﺷﻜﺎﻻت وارد ﺑﺮ ﭘﻴﻮﻧﺪ و اﺳﺘﻨﺎد
z ﻣﺴﺎﺋﻞ زﺑز ﺎﻧﺎﻧﻲ
z ﻣﺴﺎﺋﻞ ﻣﻮﺗﻮرﻫﺎي ﺑﻪﻛﺎوش ﻋﻨﻮان اﺑﺰارﻫﺎي ﮔﺮدآوري
اﻃﻼﻋﺎت
z ﻋﺪم ﻋﺪم ﺷﻨﺎﺳﺎﻳﻲ ﺷﻨﺎﺳﺎﻳﻲ ﭘﻴﻮﻧﺪﻫﺎي ﭘﻴﻮﻧﺪﻫﺎي ﻣﻮﺟﻮد ﻣﻮﺟﻮد دردر ﺻﻔﺤﺎﺗﻲ ﺻﻔﺤﺎﺗﻲ اﺳﺖ اﺳﺖ ﻛﻪﻛﻪ ﺑﺎﺑﺎ اﺳﺘﻔﺎده اﺳﺘﻔﺎده
از زﺑﺎن ﺑﺮﻧﺎﻣﻪﻧﻮﻳﺴﻲ ﺟﺎوا ﻃﺮاﺣﻲ ﺷﺪه-اﻧﺪ Java Script
zz ﻋﺪم دﺳﺘﺘﺮﺳﻲ ﺑﻪ اﻃﻼﻋ اﻃﻼ ﺎﺗﺎﺗﻲ ﻛﻛﻪ در يﭘﺎﻳﺎ ﮕﺎﮕﺎه ﻲﻫﺎﺎ اﻃﻼﻋ اﻃﻼ ﺎﺗﺎﺗ درج
ﺷﺪه و ﻧﻴﺎز ﺑﻪ رﻣﺰ ﻋﺒﻮر دارﻧﺪ
z ﻧﺎﻣﺮﺋﻲوب
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
6767وﻳﮋﮔﻲ وﻳﮋﮔﻲ ﻣﺤﻴﻂ ﻣﺤﻴﻂ ﻫﺎي ﻫﺎي اﺟﺘﻤﺎﻋﻲ اﺟﺘﻤﺎﻋﻲ ﻣﺠﺎزي ﻣﺠﺎزي
Conclusion:
A reinforcement cycle forms: people
contribute contribute more are rewarded gain more more, are rewarded, gain more
experience, improve their performance
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
6868وﻳﮋﮔﻲ وﻳﮋﮔﻲ ﻣﺤﻴﻂ ﻣﺤﻴﻂ ﻫﺎي ﻫﺎي اﺟﺘﻤﺎﻋﻲ اﺟﺘﻤﺎﻋﻲ ﻣﺠﺎزي ﻣﺠﺎزي
Friendship degree:
1= Haven’t met yet
2= Acquaintance
3= CouchSurfing
friend
4= Friend
5= Good friend
6= Cl Cl f i d ose friend
7= Best friend
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
6969وﻳﮋﮔﻲ وﻳﮋﮔﻲ ﻣﺤﻴﻂ ﻣﺤﻴﻂ ﻫﺎي ﻫﺎي اﺟﺘﻤﺎﻋﻲ اﺟﺘﻤﺎﻋﻲ ﻣﺠﺎزي ﻣﺠﺎزي
Conclusion:
Friendship degree information is beneficial
Global measures may be useful in assigning overall reputation scores, but not for
predicting if a specific person will vouch for another or not
Further work is needed to determine if vouches are given too freely
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
7070وﻳﮋﮔﻲ وﻳﮋﮔﻲ ﻣﺤﻴﻂ ﻣﺤﻴﻂ ﻫﺎي ﻫﺎي اﺟﺘﻤﺎﻋﻲ اﺟﺘﻤﺎﻋﻲ ﻣﺠﺎزي ﻣﺠﺎزي
If we focus on patents and natural science publications that have had at least a
given level of impact, we consistently observe that citing across community
boundaries leads to slightly higher impact
Correlations Correlations between between impact impact and and community community proximity proximity
boundaries leads to slightly higher impact.
*** *** and and * denote significance at < * denote significance at < 00.001 001 and and >> 00.0505 level level respectively respectively.
Conclusion: A publication’s citing across disciplines is tied to its subsequent impact.
Whil While ri ki isking not b i being ci d ited at allll, patents andd publi i blications i h l i in the natural sciences are
more likely be higher impact when they cite across community boundaries
There is no such effect in the social sciences and humanities. ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ هﺎﯼ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ
7171وﻳﮋﮔﻲ وﻳﮋﮔﻲ ﻣﺤﻴﻂ ﻣﺤﻴﻂ ﻫﺎي ﻫﺎي اﺟﺘﻤﺎﻋﻲ اﺟﺘﻤﺎﻋﻲ ﻣﺠﺎزي ﻣﺠﺎزي
Conclusion:
Friendship degree information is beneficial
Global measures may be useful in assigning overall reputation scores, but not for
predicting if a specific person will vouch for another or not
Further work is needed to determine if vouches are given too freely
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
7272ﺷﺒﻜﻪ ﺷﺒﻜﻪ ﺟﻬﺎن ﺟﻬﺎن ﻫﺎي ﻫﺎي ﻛﻮﭼﻚ
z ﺧﺎﺻﻴﻴﺖ ﺟﻬﺎﺟﻬ نن ﻛﻮﭼ ﻮﭼﻚ ﺑﺑﻪ زﺑﺎن زﺑ ن ﺳﺎده ﺑﻴﺎن ﺑﻴ ن ﻣﻲدارد ﻛﻪ ﻫﺮ دو اﻧﺴﺎﻧ ﻲ ر ﺮ و ﻲﻲ ﺑﺮ ﺑﺮ
روي زﻣﻴﻦ ﺣﺪاﻛﺜﺮ ﺑﺎ ﺷﺶ ﻓﺎﺻﻠﻪ ﺑﺎ ﻫﻢ آﺷﻨﺎ ﻫﺴﺘﻨﺪ
zz اﻳﺪه اﻳﺪه اوﻟﻴ اوﻟ ﻪﻪ اﻳﻦ اﻳﻦ ﭘﺪﻳﺪه ﭘﺪﻳﺪه ﺗﻮﺳﻂ ﺗﻮﺳﻂ ﻳﻚ ﻳﻚ ﻧﻮﻳﺴ ﻧﻮﻳ ﻨﺪه ﻨﺪه ﻣﺠﺎر ﻣﺠﺎ ﺳﺘﺎﻧ ﺳﺘﺎﻧﻲ ددر 1929 1929 ﻣﻄﺮ ﻣﻄ حح
Frigyes Karinthy ﺷﺪ
zz ﺑﺮااي او ا ﻟﻟﻴﻦ ﺑﺎر ﺗﻮﺳ ﺎ ﻂﻂ Stanley Stanley Milgram Milgram در 1967 1967 آزﻣﺎ آ ﺎﻳﺶ ﺷﺷﺪ
اوﻟﻴﻦ Duncan J. Watts and Steven Strogatz 1998 در z
ﻣﺪل ﺑﺮاي ﺷﺒﻜﻪ اي ﺑﺎ اﻳﻦ ﺧﺼﻴﺖ را اراﺋﻪ ﻛﺮدﻧﺪ
z ﻣﺪل آﻧﻬﺎ ﻧﺸﺎن داد ﻛﻪ ﺑﺎ ﺗﻌﻮﻳﺾ ﻛﺮدن ﭼﻨﺪ ارﺗﺒﺎط ﺗﺼﺎدﻓﻲ و ﺗﺸﻜﻴﻞ
ارﺗﺒﺎط ﺑﻴﻦ ﮔﺮه ﻫﺎي دور در ﻳﻚ ﮔﺮاف ﻣﻨﻈﻢ ﻣﻲﺗﻮان ﻳﻚ ﺷﺒﻜﻪ ﺟﻬﺎن
ﻛﻮﭼﻚ ﺗﻮﻟﻴﺪ ﻛﺮد
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
7373روش روشﻫﺎي ﻫﺎي ﻣﻄﺎﻟﻌﻪ ﻣﻄﺎﻟﻌﻪ رﺷﺪ رﺷﺪ داﻧﺶ داﻧﺶ
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
7474ﻛﺎرﺑﺮدﻫﺎي ﻛﺎرﺑﺮدﻫﺎي ﻓﺮاداده ﻓﺮاداده ﻫﺎي ﻫﺎي راﺑﻄﻪ راﺑﻄﻪ اي اي
Technologies that “capture” communities’ relational meta-data z
(Pingback and trackback in interblog networks, blogrolls, data
provenance)
Technologies to “tag” communities’ relational metadata (from Dublin z
Core taxonomies to folksonomies (‘wisdom of crowds’) like
Tagging Tagging pictures (Flickr) pictures (Flickr) |
Social bookmarking (del.icio.us, LookupThis, BlinkList) |
Social citations (CiteULike.org) |
SS ( ocial libraries (discogs.com, LibraryThing.com)) |
Social shopping (SwagRoll, Kaboodle, thethingsiwant.com) |
Social networks (FOAF, XFN, MySpace, Facebook) |
Technologies to “manifest” communities’ relational metadata z
(Tagclouds, Recommender systems, Rating/Reputation systems,
ISI’s Hi Hi tCit stCite, NN t k Vi li ti t ) etwork Visualization systems)
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
7575ﺟﻬﺎن ﺟﻬﺎن ﻫﺎي ﻛﻮﭼﻚ
Industries with small world network structures are more innovative! z
Networks where people spend most of their time communicating |
with one another in a group (“cluster”) and spend some time
communii ti ith th t id (“ h t t ”) cating with others outside (“short cuts”)
Small world networks exhibit high levels of “clustering” and few |
“shortcuts shortcuts”
Clusters engender trust and control, maximize capability for z
exploitation
Kelips Layout
Shortcuts engender unique combinations of network z
resources, maximize capacity for exploration
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
7676رواﺑﻂ رواﺑﻂ ﺷﺒﻜﻪ اي
Social Exchang y ge Theory: Individuals are more z
likely to reciprocate communication ties with
those who have created ties with them
previously.
Reciprocity/Mutuality |
Balance Theory: Individuals are more likely to z
create ties with people their contacts
communicate with.
Increase Balance |
Reduce Reduce Actors at Distance Two Actors at Distance Two |
Cognitive Cognitive theories theories:: Individuals are more likely to Individuals are more likely to z
create ties with people who they perceive to be
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ experts ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
7777رواﺑﻂ ﺷﺒﻜﻪ اي
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
7878رواﺑﻂ ﺷﺒﻜﻪ اي
Client
The Client-Server Model
The Peer-to-Peer Model
Client
Client
Server
Client
Client
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
7979رواﺑﻂ ﺷﺒﻜﻪ اي
Parameter Estimate Standard Error
Density (Outdegree)
-1.08 0.15
Reciprocity 0.29 0.15
Balance 3.07 1.24
Linking p g to Expert 0.04 0.01
T1-T2 Rate Parameter 1.25 0.11
TT22-TT33 Rate Rate parameter parameter 11.3232 00.1212
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
8080رواﺑﻂ ﺷﺒﻜﻪ اي
Guild members tend NOT to z
ask for advice from other
guild members over time
(self interest)
I J I
X J
(self-interest).
Guild members tend to z
reciprocate advice ties with
other members over time.
( i l h )
I J I J
(social exchange)
Guild members tend to get z
K K
Guild members tend to get
advice from the person who
gives advice to the person
they ask for advice over time.
(b l t iti it )
I
J
I
J
(balance, transitivity)
Time 1 Time 2
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
8181ﺧﻼﺻﻪ ﺧﻼﺻﻪ رواﺑﻂ رواﺑﻂ ﺷﺒﻜﻪ ﺷﺒﻜﻪ اي
Research on the dynamics of networks is well poised to make a
quantum intellectual leap by facilitating collaboration that leverages
recent advances in:
Theories about the social motivations for creating, maintaining,
dissolving and re-creating social network ties
Development of cyberinfrastructure/Web 2.0 provide the technological
capability to capture relational metadata needed to more effectively
undd d ( d bl ) i i erstand (and enable) communities.
Comp g q y putational modeling techniques to model network dynamics in
large-scale multi-agent systems
Exponential Exponential random graph modeling techniques to empirically validate random graph modeling techniques to empirically validate
the local structural signatures that explain emergent global network
propertiesproperties
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
8282روش روشﻫﺎي ﻫﺎي ﻣﻄﺎﻟﻌﻪ ﻣﻄﺎﻟﻌﻪ رﺷﺪ رﺷﺪ داﻧﺶ داﻧﺶ
z ﺷﺒﻜﻪ ﻫﺎي اﺟﺘﻤﺎﻋﻲﻲ
Weak ties, structural holes, knowledge diffusion z
z ﺷﺒﻜﻪ ﻫﺎي ﻓﻜﺮي Intellectual networks
RR h f t i t ll t l b t l l ti esearch fronts, intellectual bases, conceptual revolutions, z
paradigm shifts, turning points
z ﺷﺒﻜﻪ ﻫﺎي ﻫﻢ ﺗﺎﻟﻴﻔﻲ Co-authorship network
Citation networks, co-citation network, hybrid networks z
z ﺷﺒﻜﻪ ﻫﺎي اﺳﺘﻨﺎدي
Conceptual Conceptual revolutions: string theory; accelerating universe revolutions: string theory; accelerating universe z
Scientific debates: mass extinctions; global warming z
Response to external events: terrorist attacks z
Scientific Scientific evidence: NSAID or evidence: NSAID or Vioxx Vioxx z
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
8383SS i l N t k ocial Networks:
Weak ties and Structural Holes
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
8484SS i l N t k f C th hi ocial Network of Coauthorship
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
85853
Weak
Components
1
2
B
C
A
Betweenness
Centrality
Structural Hole
Measures
Core/Periphery Class
Density matrix
1 2
----- -----
1 0.280 0.007
2 0.007 0.002
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
8686اﻟﮕﻮﻫﺎي اﻟﮕﻮﻫﺎي ﺳﺎﺧﺘﺎري ﺳﺎﺧﺘﺎري وو زﻣﺎﻧﻲ
z آﻳﺎ ﻧﻘﺸﻪ ﻫﺎ ﻧﻤﺎﻳﺶ درﺳﺘﻲ از ﺷﺎﺧﻪ ﻫﺎي داﻧﺶ و ﻣﺠﻤﻮع ﺑﺪﻧﻪ واﺣﺪ داﻧﺶ ﻫﺴﺘﻨﺪ؟ ﭼﻪ راﻫﻬﺎﻳﻲ ﺑﺮاي
ﺳﻨﺠﺶ ﺳﻨﺠﺶ اﻋﺘﺒﺎر اﻋﺘﺒﺎر ﻧﻘﺸﻪ ﻧﻘﺸﻪ ﻫﺎي ﻫﺎي ﻋﻠﻤ ﻋﻠﻤﻲ ﻫﺴﺖ؟ ﻫﺴﺖ؟
Terrorism (1990-2004), domain experts at pivotal points |
String theory (1990-2004), domain experts at pivotal points |
zz اﻳﻦ اﻳﻦ ﻧﻘﺸﻪ ﻧﻘﺸﻪ ﻫﺎﻫﺎ ﭼﻪﭼﻪ ﺣﻘﺎﻳﻖ ﺣﻘﺎﻳﻖ اﺟﺘﻤﺎﻋ اﺟﺘﻤﺎﻋﻲ وو ﻓﻜﺮي ﻓﻜﺮي رارا ﺗﺤﺖ ﺗﺤﺖ ﭘﻮﺷﺶ ﭘﻮﺷﺶ ﻗﺮار ﻗﺮار ﻣﻣﻲ دﻫﻨﺪ؟ دﻫﻨﺪ؟
IST co-authorship (1990-2005) |
z آﻳﺎ اﺧﺘﻼف ﻧﻈﺮﻫﺎي ﻋﻠﻤﻲ را ﻣﻲ ﺗﻮان از ﻃﺮﻳﻖ ﻧﻘﺸﻪ ﻫﺎي ﻋﻠﻤﻲ ﻧﺸﺎن داد؟
Global Global warming debates warming debates |
Mass extinctions debates |
Vioxx, evidence |
zz آﻳﺎ آﻳﺎ ﻧﻘﺸﻪ ﻧﻘﺸﻪ ﻫﺎي ﻫﺎي ﻋﻠﻤ ﻋﻠﻤﻲ ﻣﻣﻲ ﺗﻮاﻧﻨﺪ ﺗﻮاﻧﻨﺪ ﺗﺎرﻳﺨﭽﻪ ﺗﺎرﻳﺨﭽﻪ ﻳﻚ ﻳﻚ ﺣﻮزه ﺣﻮزه ﻣﻄﺎﻟﻌﺎﺗ ﻣﻄﺎﻟﻌﺎﺗﻲ رارا ﺑﺎزﺳﺎزي ﺑﺎزﺳﺎزي ﻛﻨﻨﺪ؟ ﻛﻨﻨﺪ؟
Terrorism, Mass extinctions |
z آﻳﺎ ﻧﻘﺸﻪ ﻫﺎي ﻋﻠﻤﻲ ﻋﻠﻢ را ﺑﻪ ﻋﻨﻮان ﻳﻚ ﺑﺪﻧﻪ واﺣﺪ ﻓﻜﺮي ﻧﺸﺎن ﻣﻲ دﻫﻨﺪ ﻳﺎ ﻣﻨﻌﻜﺲ ﻛﻨﻨﺪه ﺣﺮﻛﺖ
ﻫﺎي ﻋﻠﻤﻲ ي ﻲ ﺟﺰﻳﺮ ﺟﺰﻳﺮه ايي ﻫﺴﺘﻨﺪ؟
z ﻣﺨﺎﻃﺐ ﻧﻘﺸﻪ ﻫﺎي ﻋﻠﻤﻲ ﭼﻪ اﻓﺮاد و ﻳﺎ ﺳﺎزﻣﺎن ﻫﺎﻳﻲ ﻫﺴﺘﻨﺪ؟
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
8787Intellectual Intellectual Networks Networks
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
8888The The Approch Approch
Structural Structural and Temporal Analysis and Temporal Analysis z
Intellectual turning points |
Emerging Emerging themes themes |
before … after!
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
8989Why Scientists Scientists Cite? Cite?
Normative Normative View View z
Citations are made because of the intellectual values |
of of cited works. cited works.
They should not be affected by social and cultural |
characteristics such as race, gender, or academic
rank.
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
9090ﭼﺮاﭼﺮا داﻧﺸﻤﻨﺪان داﻧﺸﻤﻨﺪان اﺳﺘﻨﺎد اﺳﺘﻨﺎد ﻣﻲ ﻣﻲ ﻛﻨﻨﺪ؟ ﻛﻨﻨﺪ؟
Social Social Constructivist View Constructivist Viewاﺟﺘﻤﺎﻋﻲ ﺳﺎزﻧﺪه ﺳﺎزﻧﺪه دﻳﺪﮔﺎه دﻳﺪﮔﺎه z
| ﻋﻠﻢ ﺑﺼﻮرت اﺟﺘﻤﺎﻋﻲ ﺳﺎﺧﺘﻪ ﻣﻲ ﺷﻮد و ﺗﻮﺳﻂ ﺳﻴﺎﺳﺘﮕﺰاران ﺟﺎﻣﻌﻪ ﻣﻮرد
ﺣﻤﺎﻳﺖ و ﻳ و ﺗﺸﻮﻳﻖ ﻮﻳﻖ ﻗﺮارﺮ ر ﻣﻲﻲ ﮔﻴﺮﻴﺮد.
| داﻧﺸﻤﻨﺪان از اﺳﺘﻨﺎد اﺳﺎﺳﺎ ﺑﺮاي ﺗﺎﻛﻴﺪ و ﺣﻤﺎﻳﺖ از دﻳﮕﺮ ﻣﻨﺎﺑﻊ اﺳﺘﻔﺎده ﻣﻲ
ﻛﻨﻨﺪ.
| اﺳﺘﻨﺎد ﻧﺸﺎﻧﻪ اي از ﺣﻤﺎﻳﺖ ﺳﺮﺷﻨﺎﺳﺎن ﻳﻚ رﺷﺘﻪ از ﻧﻮﺷﺘﻪ/ ﭘﮋوﻫﺸﮕﺮ ﺣﺎﺿﺮ
اﺳﺖ.
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
9191ﭼﺮا داﻧﺸﻤﻨﺪان اﺳﺘﻨﺎد ﻣﻲ ﻛﻨﻨﺪ؟
z ﭼﮕﻮﻧﻪ ؟
ﭼﺮا داﻧﺸﻤﻨﺪان اﺳﺘﻨﺎد ﻣﻲ ﻛﻨﻨﺪ؟
ﭼ ﻮ
Stewart, J. A. Drifting Continents and Colliding Paradigms: |
Perspectives on the Geoscience Revolution. Indiana University
Press, 1990.
Baldi, S. Normative versus social constructivist processes in the |
allocation of citations: A network-analytic model. American
Sociological Sociological Review Review, 6363 ((66)). 829 829-846 846.
White, H.D., Wellman, B. and Nazer, N. Does citation reflect |
social structure? Longitudinal evidence from the 'Gobenet'
interdisciplinary interdisciplinary research group research group. Journal Journal of the American Society of the American Society
for Information Science and Technology, 55 (2). 111-126.
z داﻧﺸﻤﻨﺪان ﺑﻪ دﻟﻴﻞ ارزش ﻓﻜﺮي ﻣﻨﺎﺑﻊ ﺗﻤﺎﻳﻞ ﺑﻪ اﺳﺘﻨﺎد ﺑﻪ آﻧﻬﺎ دارﻧﺪ.
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
9292ﭘﮋوﻫﺸﮕﺮان ﺑﻪ ﭼﻪ ﭼﻴﺰﻫﺎﻳﻲ اﺳﺘﻨﺎد ﻣﻲ ﻛﻨﻨﺪ؟
Foundational papersﻛﻼﺳﻴﻚ ﻣﻘﺎﻻت z
ﭘﮋوﻫﺸﮕﺮان ﺑﻪ ﭼﻪ ﭼﻴﺰﻫﺎﻳﻲ اﺳﺘﻨﺎد ﻣﻲ ﻛﻨﻨﺪ؟
ﻣﻘﺎﻻت ﻛﻼﺳﻴﻚFoundational papers
Recent papers اﺧﻴﺮ ﻣﻘﺎﻻت z
ff d ti l oundational
recent
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
9393ﭼﺮا داﻧﺸﻤﻨﺪان اﺳﺘﻨﺎد ﻣﻲ ﻛﻨﻨﺪ؟
Foundational papers z
ﭼﺮا داﻧﺸﻤﻨﺪان اﺳﺘﻨﺎد ﻣﻲ ﻛﻨﻨﺪ؟
Foundational papers z
Recent papers z
Hargens, L.L. Using the Literature: Reference Networks, Reference
Contexts, and the Social Structure of Scholarship. American
Sociological Sociological Review Review, 6565 ((66)). 846 846-865 865.
foundational
recent
sociology sociology psychology , psychology physics physics biomedicine , biomedicine
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
9494Paradigm Paradigm Shift Shift
Normative z
Citations reflect intellectual values. |
Recentness z
Citations register new concepts and new |
associations.
turning point
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
9595CiteSpace
Multipartite networks z
Author, Article, Keyword |
Co-authorship, co-citation, citation |
Time Slicing z
Filter Filter out the effects of long out the effects of long--range range citations citations |
Divide and conquer |
Threshold-Based Interpolating z
SS l t th f th elect the cream of the crop across thth b d e board |
Burst Detection z
Surg , ge of node attributes, surge of link attributes |
Pruning z
Minimum Spanning Tree |
Pathfinder Pathfinder Network Scaling Network Scaling |
Graph-Theoretical Analysis and Clustering z
Centrality |
Citation Half-Life |
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
9696CiteSeerCiteSeer
ACM DLACM DL
PubMedPubMed
Topic search
“terrorism”
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
9797Design
citing co-authorship citing
g
citing
author
citing
author
co authorship
annualannual cited cited cocitit ti ation cited
author
or paper
cited
author
or paper
annual
citationscitations
topicreference
topicreference
surge
extracted extracted
reference
gg
keyword keyword
MSTMST
centralitycentrality
PathfinderPathfinder
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
9898Expected Patterns
Thematic grouping z
Intellectual turning points z
Thematic change over z
time
Abrupt changes z
associated with triggers
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
9999Validated Validated by Experts by Experts
String String Theory Theory z
Physicists |
Terrorism z
Physiatrists |
MM di i edicine |
Political Science |
Mass Extinction z
Ocean Paleontologist |
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
100100ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
101101ACA
DCA
Co-Term
Co-Authorship
(Burst)
JCA
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
102102ﺧﻼﺻﻪ ﻣﻄﺎﻟﺐ
Scientific literature reflects the underly g g ying changes
in scientific paradigms.
Deeper Deeper processing is necessary to sharpen the big processing is necessary to sharpen the big
picture of intellectual changes.
Given Given the structural and temporal scale complexity the structural and temporal scale, complexity,
and dynamics of a knowledge domain, there is still
aa long way to go to turn a challenging and long way to go to turn a challenging and
fascinating ambition to pragmatic and everyday
tools tools and applications and applications.
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
103103ﻣﻨﺎﺑﻊ
•Bialski & Batorski ((2006)) examined which factors contribute to higher trust
between CouchSurfing friends.
• Molz (2007) examined the sociological meaning of reciprocity in the context of
hospitality hospitality exchanges exchanges.
ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺷﺒﮑﻪ هﺎﯼ ﻣﺠﺎزﯼ
104104


 به نام یزدان پاک
به نام یزدان پاک